Complete React Developer in 2019 (w/ Redux, Hooks, GraphQL)
August 26, 2019

Become a Senior React Developer! Build a massive E-commerce app with Redux, Hooks, GraphQL, Context-API, Stripe, Firebase
Created by Andrei Neagoie, Yihua Zhang
Twitter - Andrei Neagoie
Udemy Link - Complete React Developer in 2019 (w/ Redux, Hooks, GraphQL)
🌟 Get all the Sections from the Udemy Course
$$(".section--title--eCwjX").map(sections => sections.textContent);Images pasted here are captured using Chrome’s Capture Screenshot Feature

Section 1: Introduction
🌟 Get titles for Section 1 & 2
$$(".curriculum-item-link--curriculum-item--KX9MD").map(
title => title.textContent
);1. Course Outline
2. Join Our Online Classroom
Join Zero to Mastery Discord Channel
3. Exercise: Meet The Community
Introduce yourself in the Discord Community
Section 2: React Key Concepts
4. React Concepts
5. The Birth of React.js
🌟 Traditional HTML, CSS and JavaScript with less cross-browser support
🌟 Files are requested and served from the browser every time

🌟 JQuery and Backbone JS along with AJAX provided the cross-browser support and handling JS much easier

🌟 In 2010, Google introduced SPA(Single Page Application) with AngularJS using concepts of MVC - Model View Controller and containers
🌟 As the size of the application grows, it becomes harder to manage the flow with many container.

🌟 In 2013, Facebook comes with React Framework to improving the drawbacks of AngularJS

🌟 Since then AngularJS evolved to Angular(Now Angular 8) and React with lots of new features.
6. Declarative vs Imperative
Imperative - Modify the DOM one by one based on the current app state using JavaScript
Declarative - This is where React is developed for, we just need say the state and how the page should look like. React will do everything for us which increases the performance of DOM manipulation.
7. Component Architecture
Install React Dev Tools from Chrome Web Store to debug the Original React Components.
8. One Way Data Flow
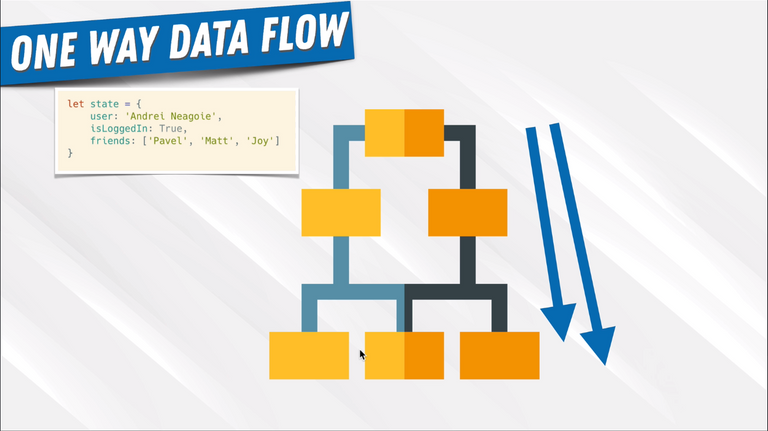
9. UI Library
10. How To Be A Great React Developer

Section 3: React Basics

🌟 Script used to get all the titles under this topic
[
...document.getElementsByClassName("curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT")
].forEach(title => {
console.log(title.textContent);
});11. Section Overview
- Learn about installing Node directly
- Learn about installing NVM-Node indirectly(I personally prefer this)
- Use CodeSandbox or StackBlitz to code online.
- Learn about Create React App
12. Environment Setup for Mac
- Install VSCode
- Install Yarn
- Install Node directly
- Install NVM-Node indirectly(I personally prefer this)
13. Environment Setup For Windows
- Install GitBash
- Install VSCode
- Install Node directly
- Install NVM-Node indirectly(I personally prefer this)
- Install Yarn
14. NPM vs YARN
🌟 Install dependencies from package.json
npm install == yarn
🌟 Install a package and add to package.json
npm install package --save == yarn add package
🌟 Install a devDependency to package.json
npm install package --save-dev == yarn add package --dev
🌟 Remove a dependency from package.json
npm uninstall package --save == yarn remove package
🌟 Upgrade a package to its latest version
npm update --save == yarn upgrade
🌟 Install a package globally
npm install package -g == yarn global add package
15. Yihua’s VSCode font and settings
- I personally love Fira Code and updated VS Code setting to use ligaments
- Install the below extension if needed,
16. Create React App
🌟 Basic app that we are going to build
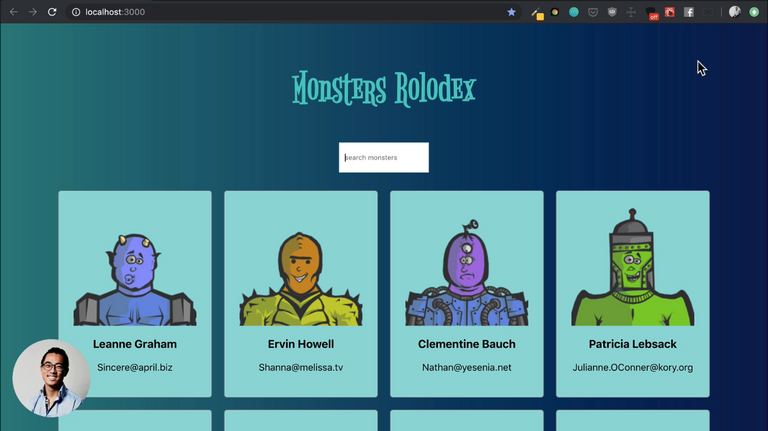
npx create-react-app monsters-rolodexcd monsters-rolodexnpm installnpm start- Hit the browser
http://localhost:8080 - Voila Starter Application is Up with Live Reload
- Uses Babel & WebPack in the background.
17. Create React App 2

package.json
{
"name": "monsters-rolodex",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"react": "^16.8.6",
"react-dom": "^16.8.6",
"react-scripts": "3.0.1"
},
"scripts": {
// start the development server
"start": "react-scripts start",
// build the project - production grade
"build": "react-scripts build",
// used of testing the react app
"test": "react-scripts test",
// eject the configurations that create react app did automatically
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
// only the configurations are ejected not the application
},
"eslintConfig": {
"extends": "react-app"
},
"browserslist": {
"production": [">0.2%", "not dead", "not op_mini all"],
"development": [
"last 1 chrome version",
"last 1 firefox version",
"last 1 safari version"
]
}
}🌟 App start from index.html
public/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
<!--
manifest.json provides metadata used when your web app is installed on a
user's mobile device or desktop. See https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/web-app-manifest/
-->
<link rel="manifest" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/manifest.json" />
<!--
Notice the use of %PUBLIC_URL% in the tags above.
It will be replaced with the URL of the `public` folder during the build.
Only files inside the `public` folder can be referenced from the HTML.
Unlike "/favicon.ico" or "favicon.ico", "%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" will
work correctly both with client-side routing and a non-root public URL.
Learn how to configure a non-root public URL by running `npm run build`.
-->
<title>React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.</noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
<!--
This HTML file is a template.
If you open it directly in the browser, you will see an empty page.
You can add webfonts, meta tags, or analytics to this file.
The build step will place the bundled scripts into the <body> tag.
To begin the development, run `npm start` or `yarn start`.
To create a production bundle, use `npm run build` or `yarn build`.
-->
</body>
</html>public folder also contains favicon.ico and manifest.json for PWA
index.html is referenced by our React app at src/index.js
src/index.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import "./index.css";
import App from "./App";
import * as serviceWorker from "./serviceWorker";
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));
// If you want your app to work offline and load faster, you can change
// unregister() to register() below. Note this comes with some pitfalls.
// Learn more about service workers: https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA
serviceWorker.unregister();ReactDOM renders our <App /> by replacing the element with id root
🌟 Global Styles and Service Workers are imported here
src/index.css
body {
margin: 0;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", "Roboto",
"Oxygen", "Ubuntu", "Cantarell", "Fira Sans", "Droid Sans",
"Helvetica Neue", sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
}
code {
font-family: source-code-pro, Menlo, Monaco, Consolas, "Courier New",
monospace;
}src/App.js
import React from "react";
import logo from "./logo.svg";
import "./App.css";
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<p>
Edit <code>src/App.js</code> and save to reload.
</p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn React
</a>
</header>
</div>
);
}
export default App;🌟 Root of our React Component
🌟 App.css and logo.svg are imported here
src/App.css
.App {
text-align: center;
}
.App-logo {
animation: App-logo-spin infinite 20s linear;
height: 40vmin;
pointer-events: none;
}
.App-header {
background-color: #282c34;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: calc(10px + 2vmin);
color: white;
}
.App-link {
color: #61dafb;
}
@keyframes App-logo-spin {
from {
transform: rotate(0deg);
}
to {
transform: rotate(360deg);
}
}src/App.test.js
🌟 It is used for testing
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import App from "./App";
it("renders without crashing", () => {
const div = document.createElement("div");
ReactDOM.render(<App />, div);
ReactDOM.unmountComponentAtNode(div);
});🌟 Extras
.gitignore
# See https://help.github.com/articles/ignoring-files/ for more about ignoring files.
# dependencies
/node_modules
/.pnp
.pnp.js
# testing
/coverage
# production
/build
# misc
.DS_Store
.env.local
.env.development.local
.env.test.local
.env.production.local
npm-debug.log*
yarn-debug.log*
yarn-error.log*node_modules will be the home for our modules installed via npm.
package-lock.json will be used for checking the integrity of the packages installed.
18. React Project Setup

19. Don’t Eject
npm run eject
Gives the Webpack and other configuration that are created under-hood when creating a new react app using creat-react-app
20. Class Components
React.Component

src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";import logo from "./logo.svg";
import "./App.css";
class App extends Component { constructor() { super(); this.state = { string: "Navin" }; } render() { return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<img src={logo} className="App-logo" alt="logo" />
<p>{this.state.string} is editing this App</p> <button onClick={() => this.setState({ string: "Navi" })}> Dont like Navin - Click Me
</button>
</header>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;

- Import
{Component}fromreact - Change the
Appfunction into a class extending `Component - Utilize the
statefrom Component by acontructorfunction withsuper(). - Initialize a variable in the state using
this.state - Change the state using
this.setState()when button clickedonClick()
21. Thinking In JSX
Learned about how state rerenders the components on an event trigger.
22. Dynamic Content
🌟 Learned about displaying dynamic contents using map()
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
// import logo from "./logo.svg";
import "./App.css";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
mosters: [
{ name: "Frankenstein", id: 1 },
{ name: "Dracula", id: 2 },
{ name: "Zombie", id: 3 }
]
};
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
{this.state.mosters.map(moster => {
return <h1 key={moster.id}>{moster.name}</h1>;
})}
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;

23. Optional: map() + key attribute
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
24. Single Page Application
What is JSON? JSON Placeholder
25. Fetching Content
🌟 Learned about fetching JSON content from JSON Placeholder and update the state
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
// import logo from "./logo.svg";
import "./App.css";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: []
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
{this.state.monsters.map(monster => {
return <h1 key={monster.id}>{monster.name}</h1>;
})}
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;

26. Optional: Promises
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
27. Architecture Our App
🌟 Learned about how to file structure components and styles
28. Card List Component
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Componentsimport { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: []
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<CardList> {this.state.monsters.map(monster => { return <h1 key={monster.id}>{monster.name}</h1>; })} </CardList> </div>
);
}
}
export default App;src/components/card-list/card-list.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import "./card-list.styles.css";
export const CardList = props => {
return <div className="card-list">{props.children}</div>;
};src/components/card-list/card-list.styles.css
.card-list {
width: 85vw;
margin: 0 auto;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr;
grid-gap: 20px;
}29. Card Component

src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Components
import { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: []
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<CardList monsters={this.state.monsters} /> </div>
);
}
}
export default App;src/components/card-list/card-list.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import "./card-list.styles.css";
import { Card } from "../card/card.component";
export const CardList = props => {
return ( <div className="card-list"> {props.monsters.map(monster => ( <Card key={monster.id} monster={monster} /> ))} </div> );};src/components/card/card.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import "./card.styles.css";
export const Card = props => (
<div className="card-container">
<img
src={`https://robohash.org/${props.monster.id}?set=set2&size=180x180`}
alt="monster"
/>
<h2>{props.monster.name}</h2>
<p>{props.monster.email}</p>
</div>
);src/components/card/card.styles.css
.card-container {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
background-color: #95dada;
border: 1px solid grey;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 25px;
cursor: pointer;
transform: translateZ(0);
transition: transform 0.25s ease-out;
}
.card-container:hover {
transform: scale(1.05);
}30. Exercise: Breaking Into Components

- Make the Component as small as possible.
- Re-usability
- Flexibility
- Each component does one login makes it easier to use in other place
- Easier Testing
- With better naming we can identify the functionality of each component.
31. State vs Props
- Learned to use React Developer Tool for seeing components, states, props and keys.
- Learned about how state from one component affects other components when passed as props.
- If state changes, then all the child component will rerender.
32. SearchField State
Learned about setState.
🌟 Added Search Field to the App
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Components
import { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: [], searchField: "" };
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<input type="search" placeholder="Search monsters" onChange={e => this.setState({ searchField: e.target.value })} /> <CardList monsters={this.state.monsters} />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;33. React Events
Learned about React Synthetic Events and how they intercept HTML events.
34. Filtering State
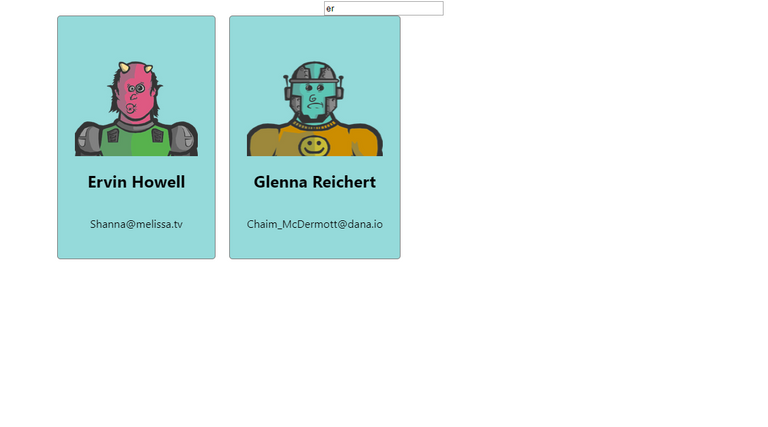
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Components
import { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: [],
searchField: ""
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
const { monsters, searchField } = this.state; const filteredMonsters = monsters.filter(monster => monster.name.toLowerCase().includes(searchField.toLowerCase()) ); return (
<div className="App">
<input
type="search"
placeholder="Search monsters"
onChange={e => this.setState({ searchField: e.target.value })}
/>
<CardList monsters={filteredMonsters} /> </div>
);
}
}
export default App;35. Optional: filter(), includes()
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
36. Search Box Component

src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Components
import { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";
import { SearchBox } from "./components/search-box/search-box.component";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: [],
searchField: ""
};
}
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
const { monsters, searchField } = this.state;
const filteredMonsters = monsters.filter(monster =>
monster.name.toLowerCase().includes(searchField.toLowerCase())
);
return (
<div className="App">
<SearchBox placeholder="Search monsters"
handleChange={e => this.setState({ searchField: e.target.value })} />
<CardList monsters={filteredMonsters} />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;src/components/search-box/search-box.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import "./search-box.styles.css";
export const SearchBox = ({ placeholder, handleChange }) => (
<input
className="search"
type="search"
placeholder={placeholder}
onChange={handleChange}
/>
);src/components/search-box/search-box.styles.css
.search {
-webkit-appearance: none;
border: none;
outline: none;
padding: 10px;
width: 150px;
line-height: 30px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
}37. Exercise: Where To Put State
🌟 Learned on where to put the state because of the one way data flow
38. Class Methods and ArrowFunctions
🌟 Learned about how this is bind to normal function and how JavaScript binds this to arrow function automatically to its context when the component gets created
src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Components
import { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";
import { SearchBox } from "./components/search-box/search-box.component";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: [],
searchField: ""
};
}
handleChange = e => { this.setState({ searchField: e.target.value }); }; componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
const { monsters, searchField } = this.state;
const filteredMonsters = monsters.filter(monster =>
monster.name.toLowerCase().includes(searchField.toLowerCase())
);
return (
<div className="App">
<SearchBox
placeholder="Search monsters"
handleChange={this.handleChange} />
<CardList monsters={filteredMonsters} />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;39. Exercise: Event Binding
🌟 Learned about Event Binding and how this works through a simple exercise
40. Quick Note: Binding in React
we learned about arrow functions and binding in React. A good rule of thumb is this: Use arrow functions on any class methods you define and aren’t part of React (i.e. render(), componentDidMount()).
If you want to learn more about this, have a read here
41. Optional: Git + GitHub
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
42. Optional: Connecting With SSH To Github
There are two ways to connect to a Github repository, through HTTPS and SSH. You can switch between the two options by clicking the switch https/ssh button after clicking clone. HTTPS does not require setup.
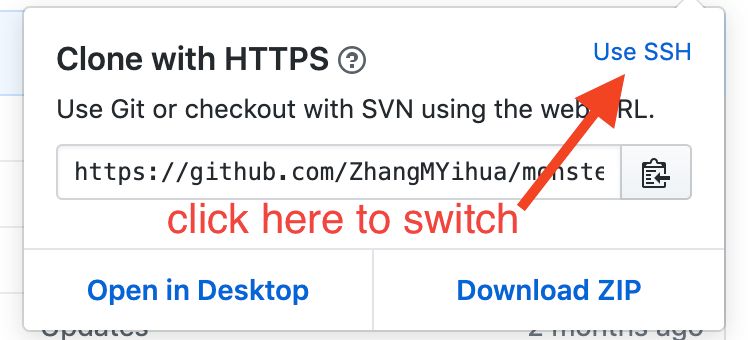
It is recommended by Github to clone using HTTPS according to their official documentation here. However, if you do end up using SSH and have never set it up before, there are a couple steps you must take first!
Firstly, SSH is like a unique fingerprint you generate for your computer in your terminal, which you then let your github account know about so it knows that requests from this computer using SSH (cloning/ pushing/ pulling) are safe to do.
In order to generate an SSH, please follow the instructions here
43. Deploying Our App

package.json
{
"name": "monsters-rolodex",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"homepage": "http://navin-moorthy.github.io/monsters-rolodex", "dependencies": {
"gh-pages": "^2.1.0", "react": "^16.8.6",
"react-dom": "^16.8.6",
"react-scripts": "3.0.1"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build",
"test": "react-scripts test",
"eject": "react-scripts eject",
"predeploy": "npm run build", "deploy": "gh-pages -d build --git git" },
"eslintConfig": {
"extends": "react-app"
},
"browserslist": {
"production": [">0.2%", "not dead", "not op_mini all"],
"development": [
"last 1 chrome version",
"last 1 firefox version",
"last 1 safari version"
]
}
}public/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000" />
<!--
manifest.json provides metadata used when your web app is installed on a
user's mobile device or desktop. See https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/web-app-manifest/
-->
<link rel="manifest" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/manifest.json" />
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Bigelow+Rules&display=swap" rel="stylesheet" /> <!--
Notice the use of %PUBLIC_URL% in the tags above.
It will be replaced with the URL of the `public` folder during the build.
Only files inside the `public` folder can be referenced from the HTML.
Unlike "/favicon.ico" or "favicon.ico", "%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico" will
work correctly both with client-side routing and a non-root public URL.
Learn how to configure a non-root public URL by running `npm run build`.
-->
<title>React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.</noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
<!--
This HTML file is a template.
If you open it directly in the browser, you will see an empty page.
You can add webfonts, meta tags, or analytics to this file.
The build step will place the bundled scripts into the <body> tag.
To begin the development, run `npm start` or `yarn start`.
To create a production bundle, use `npm run build` or `yarn build`.
-->
</body>
</html>src/index.css
body {
margin: 0;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", "Roboto",
"Oxygen", "Ubuntu", "Cantarell", "Fira Sans", "Droid Sans",
"Helvetica Neue", sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
background: linear-gradient( to left, rgba(7, 27, 82, 1) 0%, rgba(0, 128, 128, 1) 100% );}
code {
font-family: source-code-pro, Menlo, Monaco, Consolas, "Courier New",
monospace;
}src/App.js
import React, { Component } from "react";
import "./App.css";
// Components
import { CardList } from "./components/card-list/card-list.component";
import { SearchBox } from "./components/search-box/search-box.component";
class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
monsters: [],
searchField: ""
};
}
handleChange = e => {
this.setState({ searchField: e.target.value });
};
componentDidMount() {
fetch("https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users")
.then(res => res.json())
.then(users => this.setState({ monsters: users }));
}
render() {
const { monsters, searchField } = this.state;
const filteredMonsters = monsters.filter(monster =>
monster.name.toLowerCase().includes(searchField.toLowerCase())
);
return (
<div className="App">
<h1>Monsters Rolodex</h1> <SearchBox
placeholder="Search monsters"
handleChange={this.handleChange}
/>
<CardList monsters={filteredMonsters} />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;src/App.css
.App {
text-align: center;
}
h1 { font-family: "Bigelow Rules"; font-size: 72px; color: #0ccac4;}src/components/search-box/search-box.styles.css
.search {
font-size: 16px; -webkit-appearance: none;
border: none;
outline: none;
padding: 10px;
width: 200px; line-height: 30px;
margin-bottom: 30px;
border-radius: 10px;
color: white; background-color: #4dd0e1;}
.search::placeholder { color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.5);}src/components/card/card.styles.css
.card-container {
/*display: flex;*/ /*flex-direction: column;*/ background-color: #95dada;
border: 1px solid grey;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 25px;
cursor: pointer;
transform: translateZ(0);
transition: transform 0.25s ease-out;
}
.card-container:hover {
transform: scale(1.05);
}src/components/card-list/card-list.styles.css
.card-list {
width: 85vw;
margin: 0 auto;
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 1fr; grid-gap: 20px;
}
@media (min-width: 640px) { .card-list { grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; }}@media (min-width: 900px) { .card-list { grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr; }}@media (min-width: 1160px) { .card-list { grid-template-columns: 1fr 1fr 1fr 1fr; }}- Deploying to GitHub
- Served through gh-pages
- Responsive to multiple screen sizes
44. React and ReactDOM
🌟 Learned about plain React and ReactDOM in JavaScript using CDN packages
🌟 Learned what React Library does in the background with JSX syntax
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge" />
<title>React Plain</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root">React Not Rendered</div>
<script
crossorigin
src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js"
></script>
<script
crossorigin
src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js"
></script>
<script>
const Persons = props =>
React.createElement("div", {}, [
React.createElement("h2", {}, props.name),
React.createElement("p", {}, props.occupation)
]);
const App = () =>
React.createElement("div", {}, [
React.createElement(Persons, {
name: "Navin",
occupation: "Web Developer"
}),
React.createElement(Persons, {
name: "Vasanth",
occupation: "Mainframe Developer"
}),
React.createElement(Persons, {
name: "Boopalan",
occupation: "Python Developer"
})
]);
ReactDOM.render(
React.createElement(App),
document.getElementById("root")
);
</script>
</body>
</html>45. Revisiting Virtual-DOM +Unidirectional Data Flow
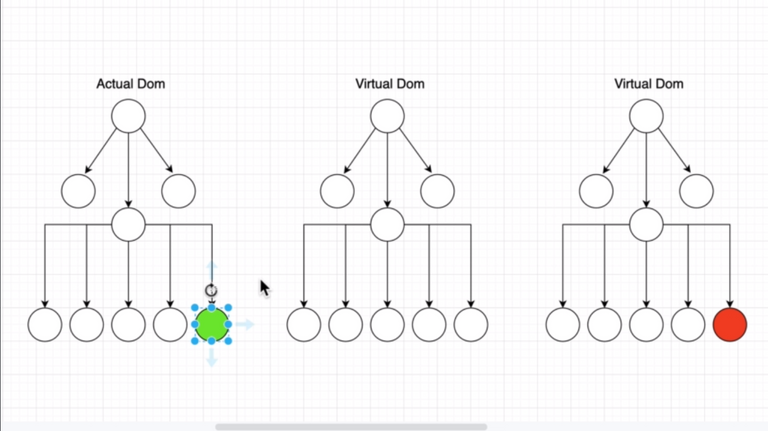
🌟 Learned the diff between Virtual DOM and DOM and how change in state changes only the affected DOM using Virtual DOM with Unidirectional Flow.
Used Chrome Dev Tool->More Tools->Rendering->Paint Flashing to see the affected part of the DOM for state changes.
46. Asynchronous setState
🌟 Learned about how state changes asynchrously and how we can make it change in respective to prevState.
47. Introducing LifeCycle Methods
- 48.Mounting
- 49.Updating
- 50.Unmounting
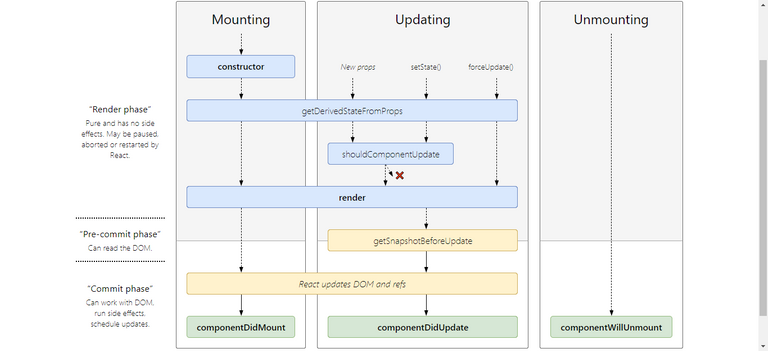
React LifeCycle Interactive Diagram
Quiz 1: When should we use a functional component vs a class com
We want to create a new component in React that doesn’t need any local state management or access to lifecycle methods in the component. What kind of component should we make?
Functional components are the best type of component to render if you don’t need access to state or LifeCycle methods! It has benefits of being easy to test, easier to read, and easier to write!
51. Section Review
🌟 Reviewed all the code done in this section
Section 4: Master Project: SettingUp E-commerce Project
🌟 Run the below code to get all the sub headings of this section
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(el => el.textContent);52. The Long Road Ahead


53. Project Overview
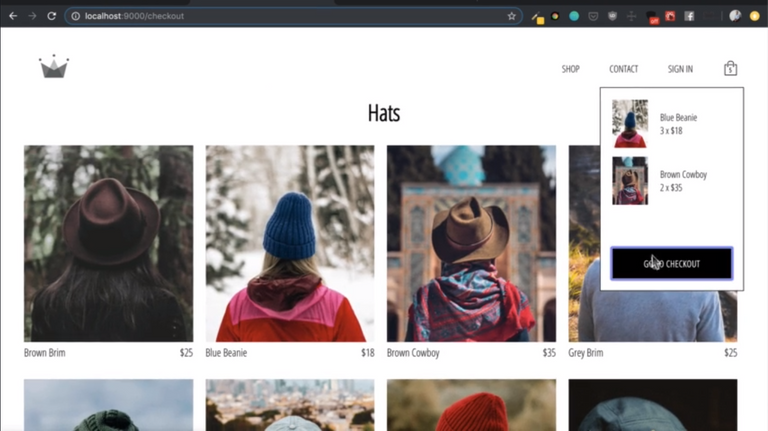
54. GitHub + Project Repositories
55. Course Guideline + GitHub Links
🌟 Instructions on how to clone and follow guide for the site
56. Quick Note About GitHub
🌟 Fork Yihua Repo and clone it to have our own repo
57. E-commerce Homepage +SASS setup
npx create-react-app crown-clothing
Removed unused codes
npm i -S node-sass
58. Project Files + Modules
🌟 Quick intro for the project files and modules that come preinstalled with create-react-app
🌟 Also learned about the troubleshooting steps when encountered an error
59. Project Component Architecture
🌟 Quick intro on folder structure and how to easily understand the components without getting lost
60. CSS and SCSS files
🌟 Note on both CSS and SCSS files will be included for use
61. Homepage and Directory Components

62. Styling Menu Items

cubic-bezier timing function - MDN
Section 5: Master Project: ReactRouter and Routing
🌟 Run the below code to get all the sub headings of this section
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(el => el.textContent);63. Routing In React
🌟 Quick intro to React Router on how it works on the browser
64. Routing In Our Project
npm install --save react-router-dom
🌟 Brief intro to React Router on how it works via react-router-dom
65. React Router DOM
🌟 Deep dive into React Router on how it works on via react-router-dom using an example repo
React Router GitHub repo example
import React from "react";
import { Route, Link } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
const HomePage = props => {
console.log(props);
return (
<div>
<button onClick={() => props.history.push("/topics")}>Topics </button> <h1>HOME PAGE</h1>
</div>
);
};
const TopicsList = props => {
return (
<div>
<h1>TOPIC LIST PAGE</h1>
<Link to={`${props.match.url}/13`}>TO TOPIC 13</Link> <Link to={`${props.match.url}/17`}>TO TOPIC 17</Link> <Link to={`${props.match.url}/21`}>TO TOPIC 21</Link> </div>
);
};
const TopicDetail = props => {
return (
<div>
<h1>TOPIC DETAIL PAGE: {props.match.params.topicId}</h1>
</div>
);
};
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Route exact path="/" component={HomePage} />
<Route exact path="/blog/asdqw/topics" component={TopicsList} />
<Route path="/blog/asdqw/topics/:topicId" component={TopicDetail} />
<Route exact path="/blog/topics" component={TopicsList} />
<Route path="/blog/topics/:topicId" component={TopicDetail} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;66. withRouter()
import React from "react";
import { withRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import "./menu-item.styles.scss";
const MenuItem = ({ title, imageUrl, size, linkUrl, history, match }) => (
<div
className={`${size} menu-item`}
onClick={() => history.push(`${match.url}${linkUrl}`)}
>
<div
style={{ backgroundImage: `url(${imageUrl})` }}
className="background-image"
/>
<div className="content">
<h1 className="title">{title.toUpperCase()}</h1>
<span className="subtitle">SHOP NOW</span>
</div>
</div>
);
export default withRouter(MenuItem);Section 6: Master Project: Forms + Components
🌟 Run the below code to get all the sub headings of this section
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(el => el.textContent);67. Shopping Data
68. Shop Page
Route: /shop

69. Collection Item
Route: /shop
70. Header Component
Route: /
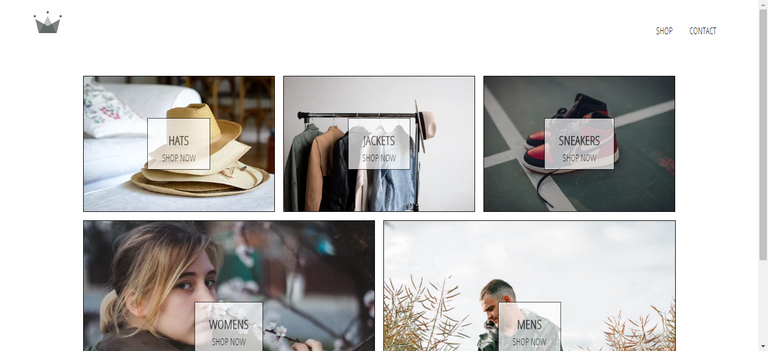
71. Resources: Importing SVG In React
72. Introducing Forms In React
🌟 Quick intro on how sign in and sign up component works and how state is managed in these components(ONLY LOCALLY)
73. Sign In Component
Route: /signin

74. Form Input Component
Route: /signin

75. Custom Button Component
Route: /signin

Section 7: Master Project: Firebase +User Authentication
🌟 Run the below code to get all the sub headings of this section
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(el => el.textContent);76. Section Overview
🌟 Quick intro on how Firebase is gonna be taught in this section
77. Firebase Introduction
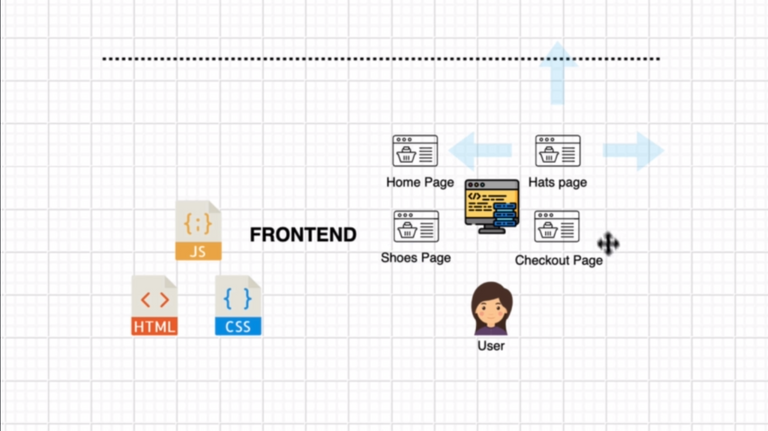
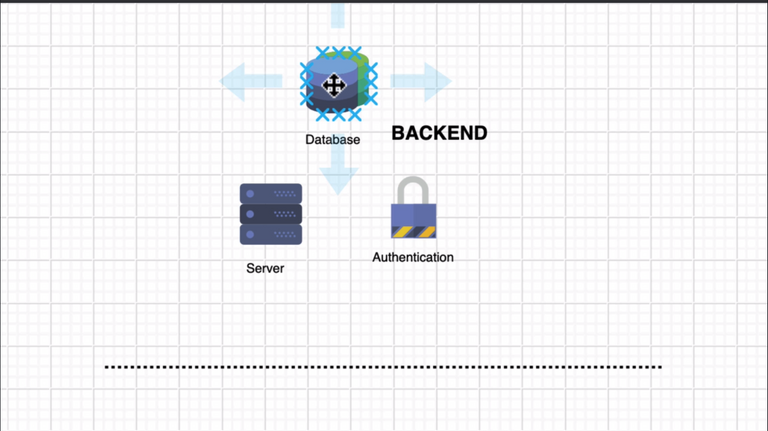
78. Adding a Project to Firebase
- Added
npm i -S firebaseto the project - Created a new firebase project “crown-clothing-db”
- Created a web app “crown-clothing-db”
- Spark plan for the web app is far more than enough
79. Note about GitHub
🌟 It is safe to enter the Firebase API in public
80. Google Sign In Authentication
Route: /signin

81. Cloning From This Point On
🌟 Nothing but a note for those who fork the original GitHub repo
82. Google Sign In Authentication 2
- Added state to look into the current user in
App.js
83. Optional: How to fix 403:restricted_client error
It’s possible you may encounter a google Authorization error that says 403:restricted_client. If you do, here are the instructions to fix it!
There should be a Learn More link in the popup, clicking that should take you to the Google APIs console that has three tabs under the header named Credentials, OAuth Consent Screen, and Domain Verification. Go to the OAuth Consent Screen tab and update the Application Name to “crwn-clothing” or any other name you’re comfortable with (i.e. the name of your project). Click on save at the bottom, then try logging into your verified Google account thereafter.
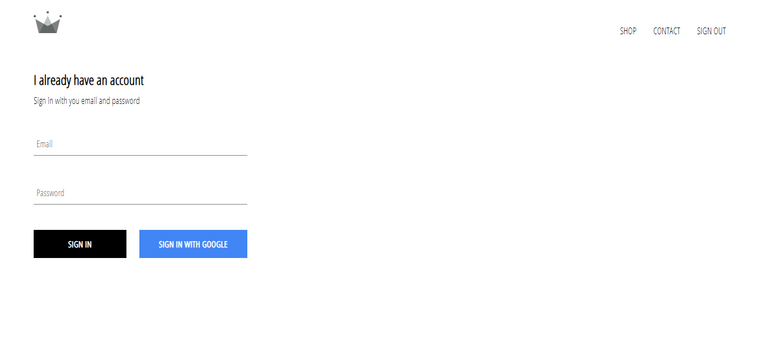
84. Google Sign In Authentication 3
Route: /signin
85. Firebase Firestore
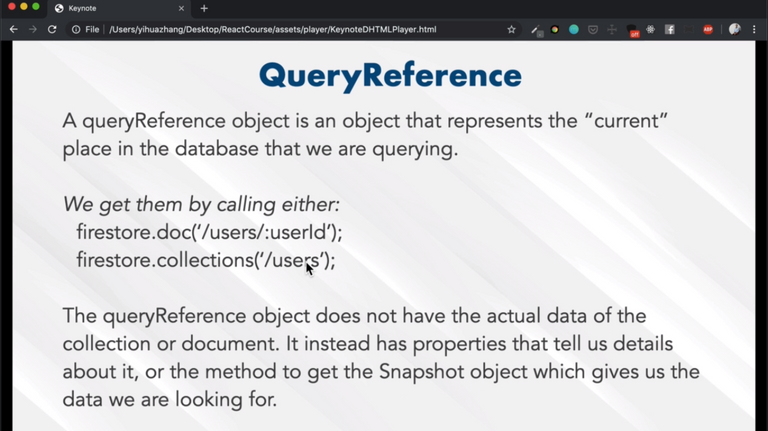
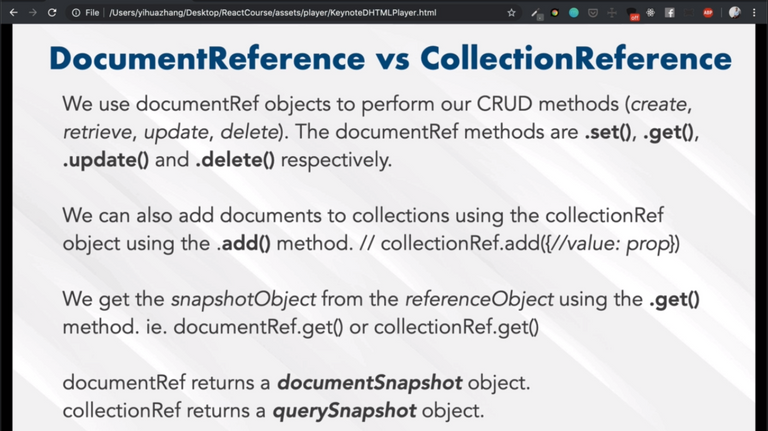
🌟 Quick intro on Firebase Firestore
Learned how to
- create Firebase database
- create collections and documents
- query for the collections and documents
86. Optional: Async Await
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
87. Storing User Data In Firebase


88. Storing User Data In Our App
src/App.js
import React from "react";
import { Switch, Route } from "react-router-dom";
import "./App.css";
import Header from "./components/header/header.component";
import HomePage from "./pages/homepage/homepage.component";
import SignInAndSignUpPage from "./pages/sign-in-and-sign-up/sign-in-and-sign-up.component";
import ShopPage from "./pages/shop/shop.component";
import { auth, createUserProfileDocument } from "./firebase/firebase.utils";
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
currentUser: null
};
}
unSubscribeFromAuth = null;
componentDidMount() { this.unSubscribeFromAuth = auth.onAuthStateChanged(async userAuth => { if (userAuth) { const userRef = await createUserProfileDocument(userAuth); userRef.onSnapshot(snapShot => { this.setState({ currentUser: { id: snapShot.id, ...snapShot.data() } }); }); } else { this.setState({ currentUser: userAuth }); } }); }
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unSubscribeFromAuth = null;
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Header currentUser={this.state.currentUser} />
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={HomePage} />
<Route exact path="/signin" component={SignInAndSignUpPage} />
<Route path="/shop" component={ShopPage} />
</Switch>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;89. Sign Up Component
import React from "react";
import "./sign-up.styles.scss";
import FormInput from "../form-input/form-input.components";
import CustomButton from "../custom-button/custom-button.components";
import { auth, createUserProfileDocument } from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
class SignUp extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
displayName: "",
email: "",
password: "",
confirmPassword: ""
};
}
handleSubmit = async event => {
event.preventDefault();
const { displayName, email, password, confirmPassword } = this.state;
if (password !== confirmPassword) {
alert("Passwords do not match");
return;
}
try {
const { user } = await auth.createUserWithEmailAndPassword(
email,
password
);
await createUserProfileDocument(user, { displayName });
this.setState({
displayName: "",
email: "",
password: "",
confirmPassword: ""
});
} catch (error) {
console.log("Error in sign up", error.message);
}
};
handelChange = event => {
const { name, value } = event.target;
this.setState({ [name]: value });
};
render() {
const { displayName, email, password, confirmPassword } = this.state;
return (
<div className="sign-up">
<h2 className="title">I do not have a account</h2>
<span>Sign up with your email and password</span>
<form className="sign-up" onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<FormInput
type="text"
name="displayName"
value={displayName}
onChange={this.handelChange}
label="Display Name"
required
/>
<FormInput
type="email"
name="email"
value={email}
onChange={this.handelChange}
label="Email"
required
/>
<FormInput
type="password"
name="password"
value={password}
onChange={this.handelChange}
label="Password"
required
/>
<FormInput
type="password"
name="confirmPassword"
value={confirmPassword}
onChange={this.handelChange}
label="Confirm Password"
required
/>
<CustomButton type="Submit">Sign Up</CustomButton>
</form>
</div>
);
}
}
export default SignUp;.sign-up {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
width: 380px;
.title {
margin: 10px 0;
}
}90. Sign Up With Email and Password
Route: /signin
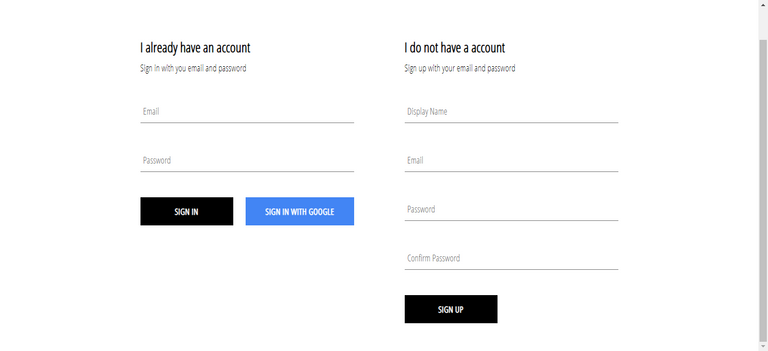
91. Sign In With Email and Password
import React from "react";
import "./sign-in.styles.scss";
import FormInput from "../form-input/form-input.components";
import CustomButton from "../custom-button/custom-button.components";
import { auth, signInWithGoogle } from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
class SignIn extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
email: "",
password: ""
};
}
handleSubmit = async e => { e.preventDefault(); const { email, password } = this.state; try { await auth.signInWithEmailAndPassword(email, password); this.setState({ email: "", password: "" }); } catch (error) { console.log("Error signing in", error.message); } };
handleChange = e => {
const { value, name } = e.target;
this.setState({ [name]: value });
};
render() {
const { email, password } = this.state;
return (
<div className="sign-in">
<h2 className="title">I already have an account</h2>
<span>Sign in with you email and password</span>
<form onSubmit={this.handleSubmit}>
<FormInput
type="email"
name="email"
value={email}
handleChange={this.handleChange}
label="Email"
required
/>
<FormInput
type="password"
name="password"
value={password}
handleChange={this.handleChange}
label="Password"
required
/>
<div className="buttons">
<CustomButton type="submit">Sign In</CustomButton>
<CustomButton onClick={signInWithGoogle} isGoogleSignIn>
Sign in with Google
</CustomButton>
</div>
</form>
</div>
);
}
}
export default SignIn;Quiz 2: Firebase unsubscribe method
Whenever we call the onAuthStateChanged() or onSnapshot() methods from our auth library or referenceObject, we get back a function that lets us unsubscribe from the listener we just instantiated. Which lifecycle method should we use to call that unsubscribe method in?
🌟 componentWillUnmount
🌟 Calling the unsubscribe function when the component is about to unmount is the best way to make sure we don’t get any memory leaks in our application related to listeners still being open even if the component that cares about the listener is no longer on the page.
92. Section Review
🌟 Quick recap on this section coding
Section 8: Master Project: Redux 1
🌟 Run the below code to get all the sub headings of this section
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(el => el.textContent);93. Section Overview
94. Redux Introduction
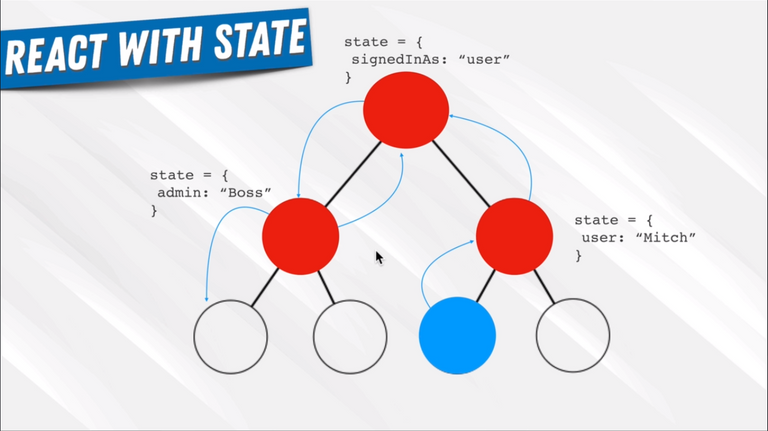
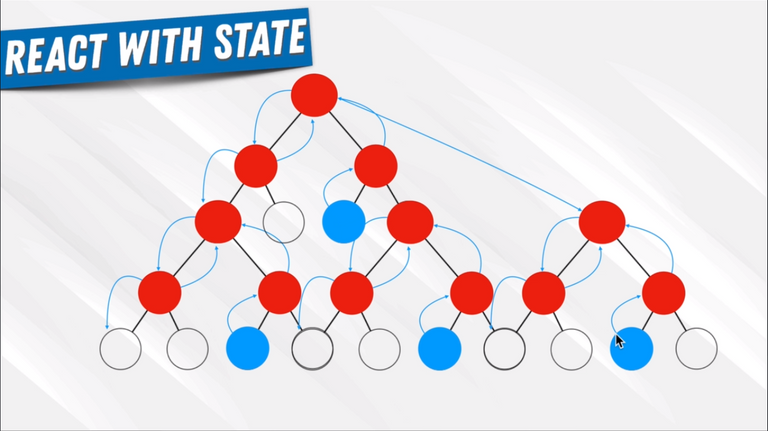
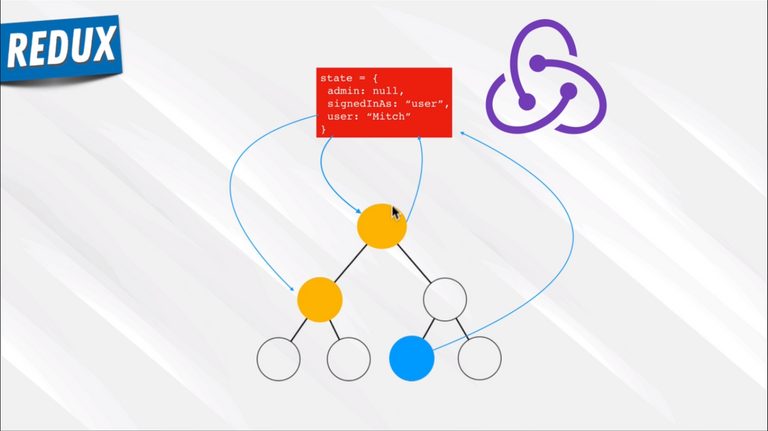
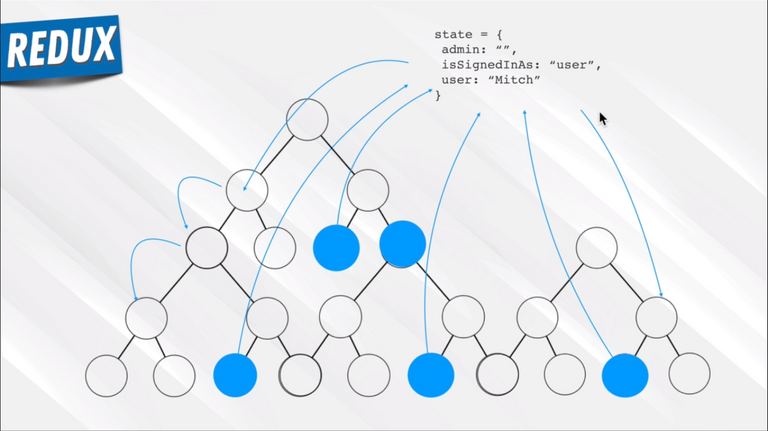
95. Redux Concepts

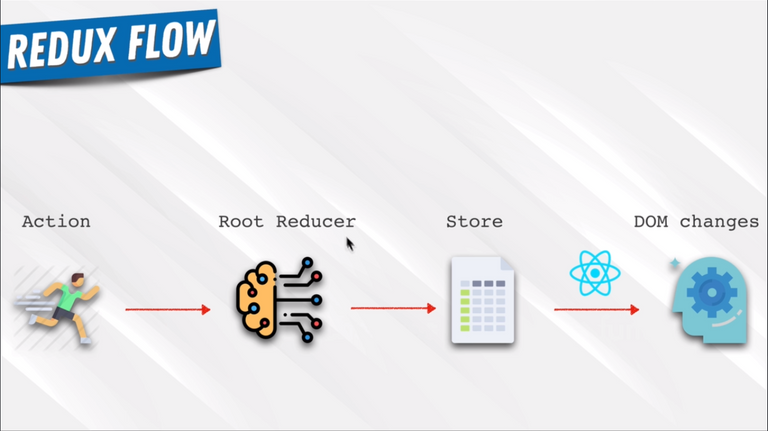
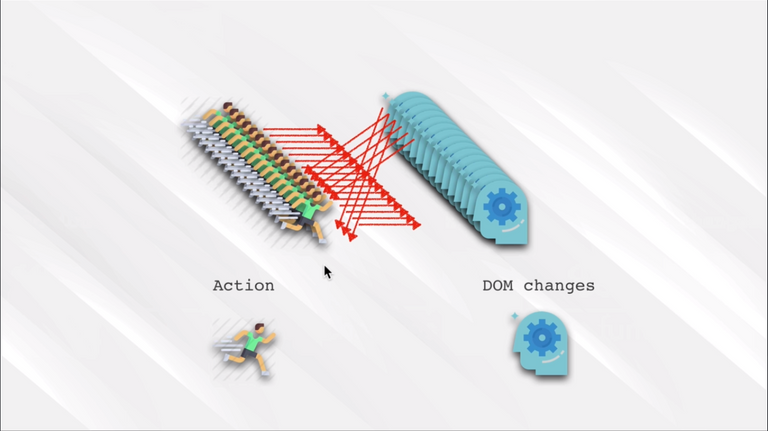
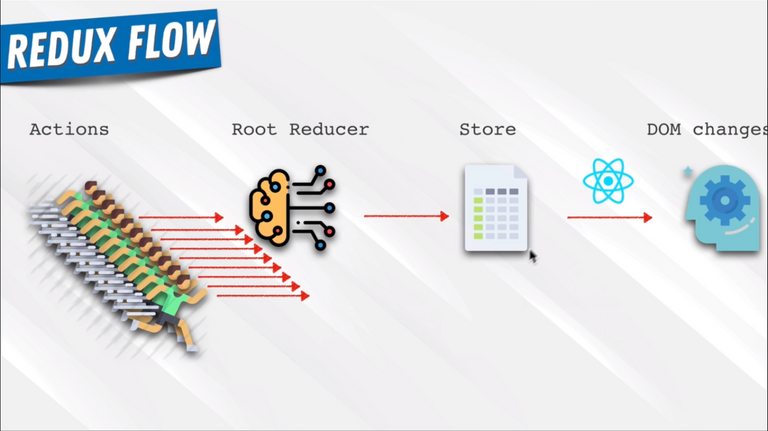
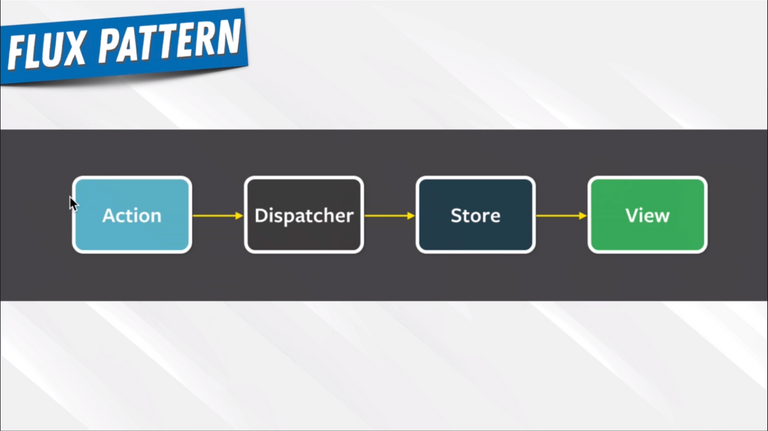
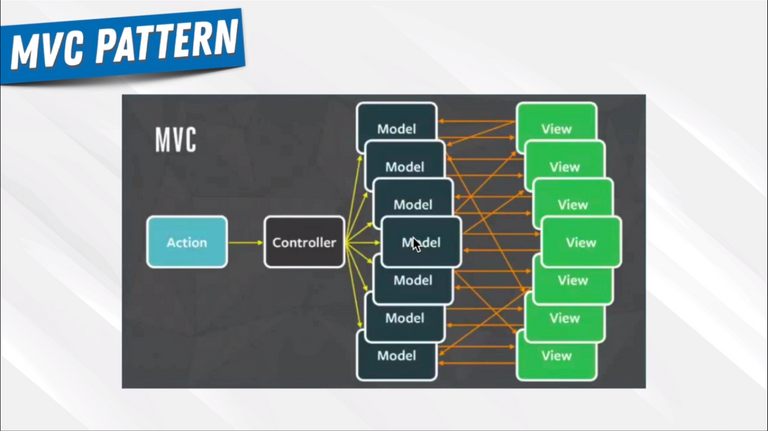
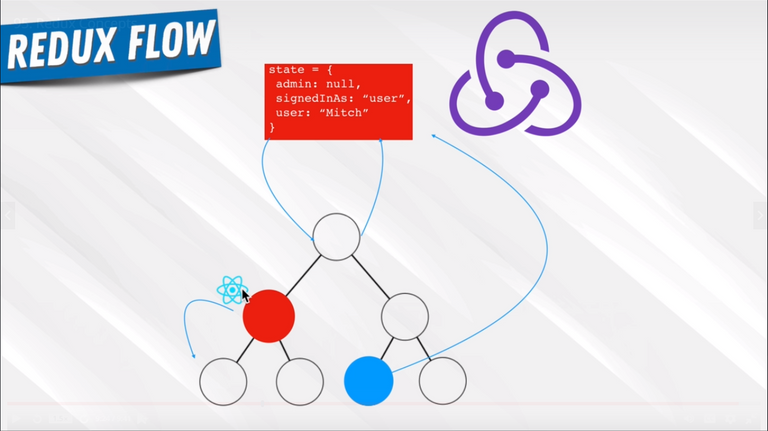
96. Redux In Our Application
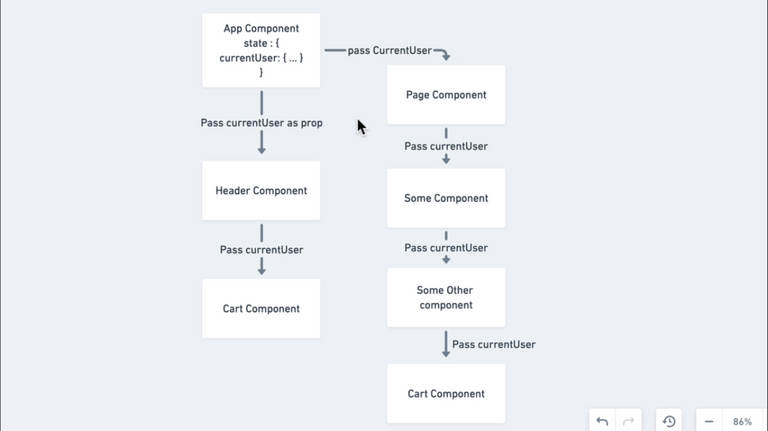
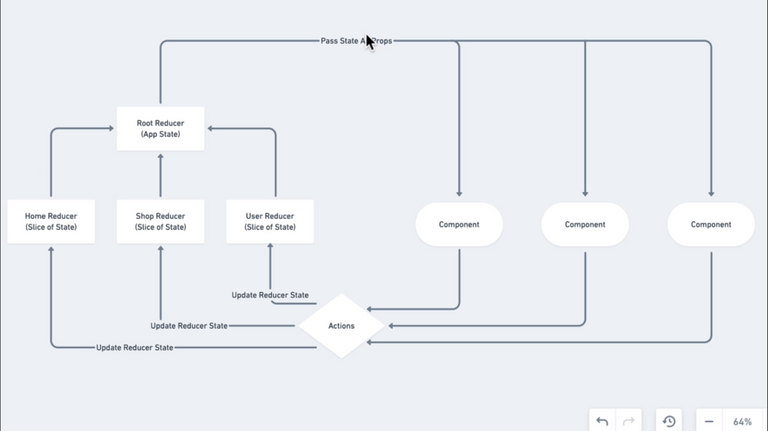
97. Redux Actions and Reducers
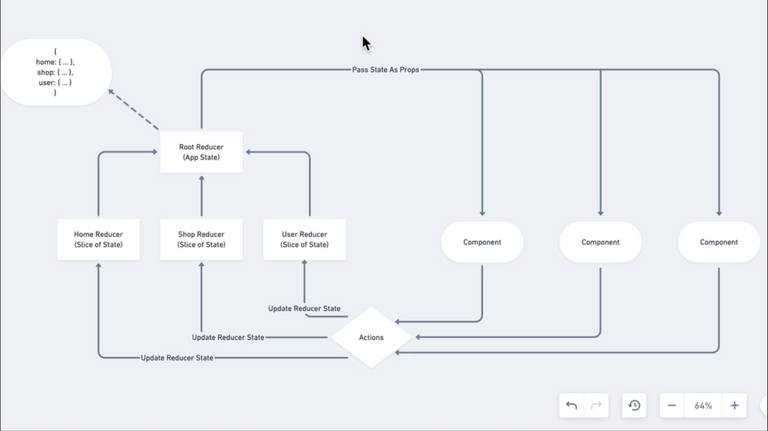
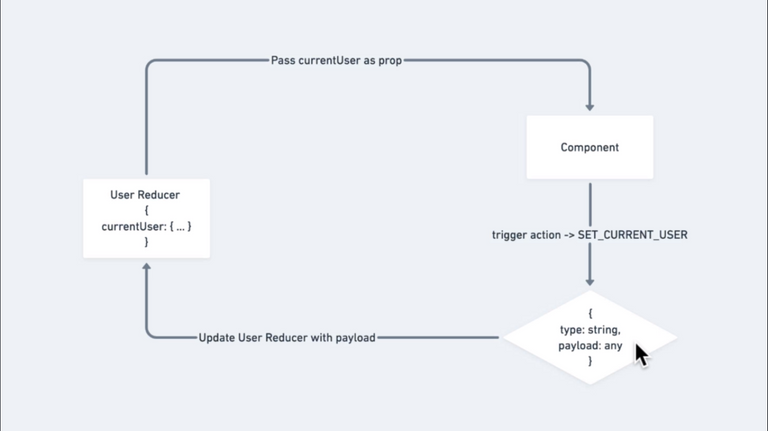
98. Setting Up Redux 1
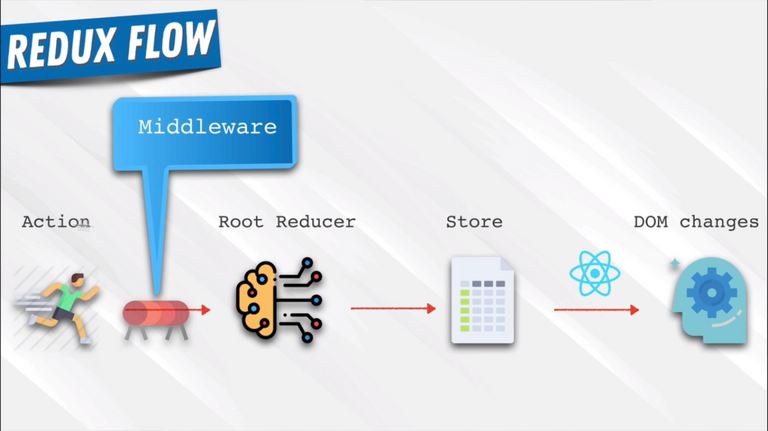
🌟 Installed below three npm packages
Redux Logger || Redux || React Redux
99. Setting Up Redux 2
src/index.js
import React from "react";
import ReactDOM from "react-dom";
import { BrowserRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import "./index.css";
import App from "./App";
import store from "./redux/store";
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>,
document.getElementById("root")
);src/redux/store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import logger from "redux-logger";
import rootReducer from "./root-reducer";
const middlewares = [logger];
const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(...middlewares));
export default store;src/redux/user/user.action.js
export const setCurrentUser = user => ({
type: "SET_CURRENT_USER",
payload: user
});100. connect() and mapStateToProps
Header Component
import React from "react";
import { Link } from "react-router-dom";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { auth } from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
import "./header.styles.scss";
import { ReactComponent as Logo } from "../../assets/crown.svg";
const Header = ({ currentUser }) => (
<div className="header">
<Link to="/">
<Logo className="logo" />
</Link>
<div className="options">
<Link to="/shop" className="option">
SHOP
</Link>
<Link to="/shop" className="option">
CONTACT
</Link>
{currentUser ? (
<div className="option" onClick={() => auth.signOut()}>
SIGN OUT
</div>
) : (
<Link className="option" to="/signin">
SIGN IN
</Link>
)}
</div>
</div>
);
const mapStatetoProps = state => ({ currentUser: state.user.currentUser});export default connect(mapStatetoProps)(Header);101. mapDispatchToProps
App Component
import React from "react";
import { Switch, Route } from "react-router-dom";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { setCurrentUser } from "./redux/user/user.action";
import "./App.css";
import Header from "./components/header/header.component";
import HomePage from "./pages/homepage/homepage.component";
import SignInAndSignUpPage from "./pages/sign-in-and-sign-up/sign-in-and-sign-up.component";
import ShopPage from "./pages/shop/shop.component";
import { auth, createUserProfileDocument } from "./firebase/firebase.utils";
class App extends React.Component {
unSubscribeFromAuth = null;
componentDidMount() {
const { setCurrentUser } = this.props;
this.unSubscribeFromAuth = auth.onAuthStateChanged(async userAuth => {
if (userAuth) {
const userRef = await createUserProfileDocument(userAuth);
userRef.onSnapshot(snapShot => {
setCurrentUser({ id: snapShot.id, ...snapShot.data() }); });
} else {
setCurrentUser(userAuth); }
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unSubscribeFromAuth = null;
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<Header />
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={HomePage} />
<Route exact path="/signin" component={SignInAndSignUpPage} />
<Route path="/shop" component={ShopPage} />
</Switch>
</div>
);
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({ setCurrentUser: user => dispatch(setCurrentUser(user))});export default connect( null, mapDispatchToProps)(App);102. User Redirect and User Action-type
🌟 Added homepage redirect if the user is already logged in
103. Cart Component

104. Card Drop-down Component

105. Implementing Redux In Cart
🌟 Conditionally render cart drop-down
106. Add To Cart Styling
Route: /shops/hats
107. Cart Item Reducer
🌟 Learned how to add items to the cart and store them in Redux
108. Adding Multiple Items To Cart
🌟 Added the quantity value to the existing Array
export const addItemToCart = (cartItems, cartItemToAdd) => {
const existingCartItem = cartItems.find(
cartItem => cartItem.id === cartItemToAdd.id
);
if (existingCartItem) {
return cartItems.map(cartItem =>
cartItem.id === cartItemToAdd.id
? { ...cartItem, quantity: cartItem.quantity + 1 }
: cartItem
);
}
return [...cartItems, { ...cartItemToAdd, quantity: 1 }];
};109. Optional: find()
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
110. Cart Item Component
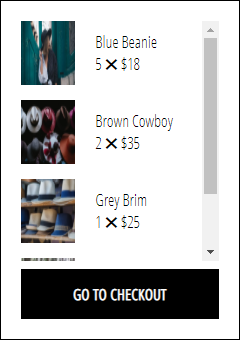
111. Optional: reduce()
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
112. Selectors in Redux
Use Reselect for Memoization in the states that are not changed in Redux
import React from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { toggleCartHidden } from "../../redux/cart/cart.actions";
import { ReactComponent as ShoppingIcon } from "../../assets/shopping-bag.svg";
import "./cart-icon.styles.scss";
const CartIcon = ({ toggleCartHidden, itemCount }) => ( <div className="cart-icon" onClick={toggleCartHidden}>
<ShoppingIcon className="shopping-icon" />
<span className="item-count">{itemCount}</span> </div>
);
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
toggleCartHidden: () => dispatch(toggleCartHidden())
});
const mapStateToProps = ({ cart: { cartItems } }) => ({ itemCount: cartItems.reduce( (accumulatedQuantity, cartItem) => accumulatedQuantity + cartItem.quantity, 0 )});
export default connect(
mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps
)(CartIcon);113. Optional: Memoization
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
114. Reselect Library
🌟 Used Memoized selectors to improve our app performance from unwanted re-renders
npm i -S reselect
import { createSelector } from "reselect";
const selectCart = state => state.cart;
export const selectCartItems = createSelector(
[selectCart],
cart => cart.cartItems
);
export const selectCartItemsCount = createSelector(
[selectCartItems],
cartItems =>
cartItems.reduce(
(accumulatedQuantity, cartItem) =>
accumulatedQuantity + cartItem.quantity,
0
)
);115. User Selectors
🌟 Used createStructuredSelector to pass the state to multiple selectors easy peacy
import { createStructuredSelector } from "reselect";
116. Checkout Page
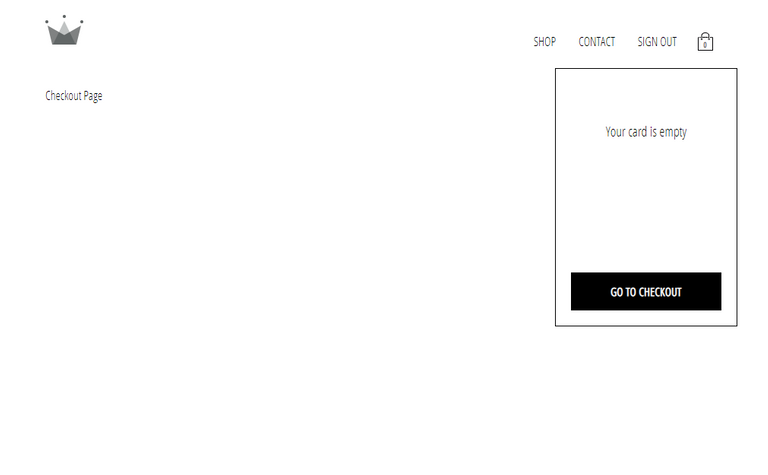
117. Checkout Page 2
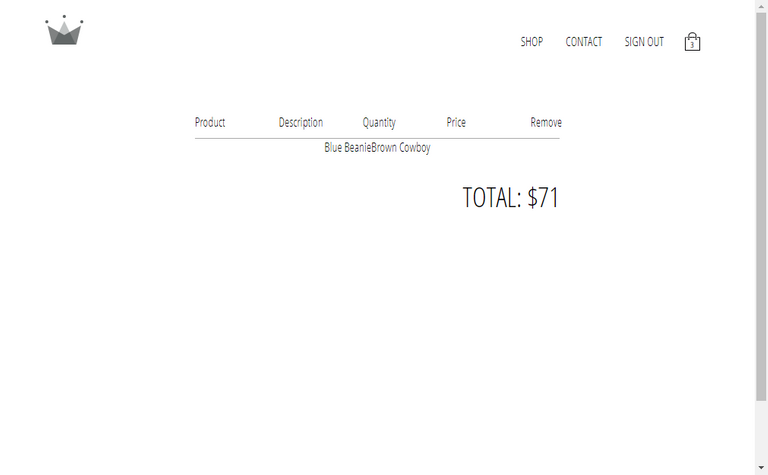
118. Extensible Code
🌟 Make code and components simple and easier that others can understand

119. Dispatch Action Shorthand
import React from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { createStructuredSelector } from "reselect";
import { withRouter } from "react-router-dom";
import CustomButton from "../custom-button/custom-button.components";
import CartItem from "../cart-item/cart-item.component";
import { toggleCartHidden } from "../../redux/cart/cart.actions";import { selectCartItems } from "../../redux/cart/cart.selectors";
import "./cart-dropdown.styles.scss";
const CartDropDown = ({ cartItems, history, dispatch }) => ( <div className="cart-dropdown">
<div className="cart-items">
{cartItems.length ? (
cartItems.map(cartItem => (
<CartItem key={cartItem.id} item={cartItem} />
))
) : (
<span className="empty-message">Your card is empty</span>
)}
</div>
<CustomButton onClick={() => { history.push("/checkout"); dispatch(toggleCartHidden()); }} > GO TO CHECKOUT
</CustomButton>
</div>
);
const mapStateToProps = createStructuredSelector({
cartItems: selectCartItems
});
export default withRouter(connect(mapStateToProps)(CartDropDown));120. Checkout Item Component
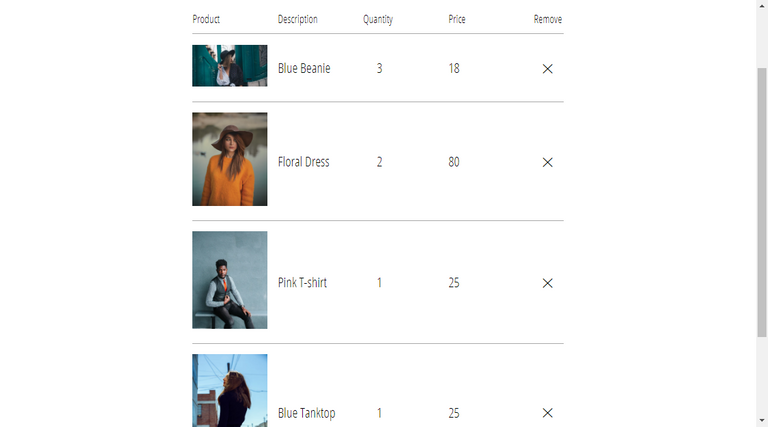
121. Remove Items From Cart
🌟 Created a remove a cartItem action to remove the item on clear button in Checkout Component
122. Remove Items At Checkout
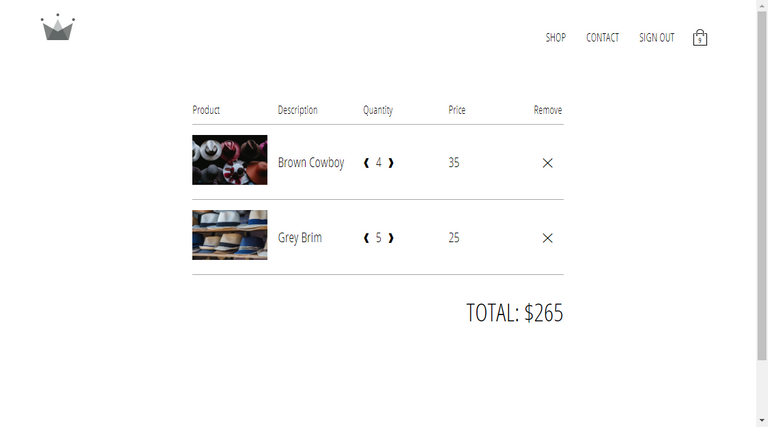
Section 9: Master Project: SessionStorage + Persistence
123. Local Storage and Session Storage
🌟 Brief intro on Local Storage and Session Storage
124. Redux Persist
🌟 Using Redux-persist we stored our cartItems in LocalStorage to persist even after the session close.
Section 10: Master Project: Redux 2
125. Directory State Into Redux
🌟 Moved Directory State Into Redux
126. Collection State Into Redux
🌟 Moved Shop Data State Into Redux
127. Collection Overview Component
🌟 Created a Collection Overview Component for /shop page
Section 11: Master Project:Advanced Routing
128. Nested Routing in Shop Page
129. Improving Naming Of Component
🌟 Changed all the naming for Category Page to Collection Page
130. Collection Routing and Selector
Route: /shop/mens
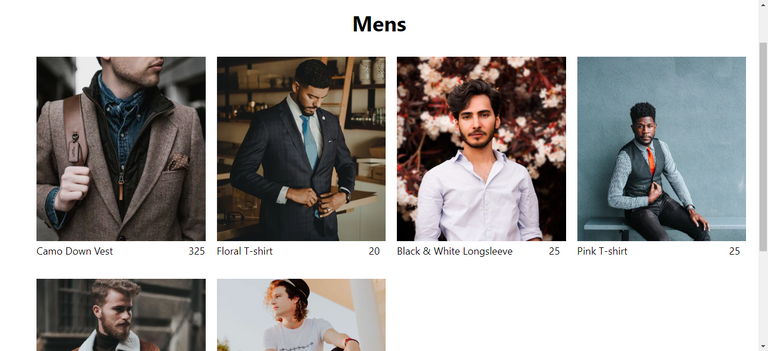
🌟 Collections are routed to its own collection using URL params
131. Optional: Currying
🌟 Explained in Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
Section 12: Master Project: StateNormalization
132. Data Normalization + Collection Page
🌟 Used data normalization to improve the performance by converting arrays to objects
133. Optional: Hash Tables vs Arrays
In the previous lesson we learned about Objects (Hash Table data structure) being better for searching for items than Array. This is a common computing optimization when talking about data structures. If you want to learn more about why this is, this is a great resource for you to use.
134. Data Flow In Our App
import { createSelector } from "reselect";
const selectShop = state => state.shop;
export const selectCollections = createSelector(
[selectShop],
shop => shop.collections
);
export const selectCollectionsForPreview = createSelector( [selectCollections], collections => Object.keys(collections).map(key => collections[key]));
export const selectCollection = collectionUrlParam =>
createSelector(
[selectCollections],
collections => collections[collectionUrlParam]
);135. Thinking About Data Flow

Section 13: Master Project: StripePayments Part 1
136. Introduction To Stripe
🌟 Quick intro on how stripe works and how they perform transactions
137. Stripe Integration
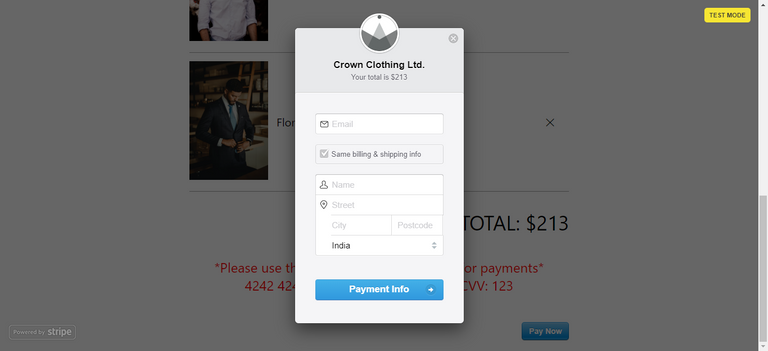
🌟 Implemented stripe checkout button
138. Cloning From This Point On
🌟 Note for those who clone the Instructors code because of the publishableKey in StripCheckoutButton
139. Finishing Touches + Look Ahead

Section 14: Master Project:Deploying To Production
140. Deploying To Heroku
Heroku Dashboard || Heroku CLI || Heroku CRA BuildPack
🌟 Install Heroku in Ubuntu
sudo snap install --classic heroku
🌟 Check Heroku version
heroku --version
🌟 Login to Heroku CLI with -i login in CLI itself with credentials
heroku login -i
🌟 Create a new project with React Buildpack
heroku create navin-navi-crown-clothing --buildpack https://github.com/mars/create-react-app-buildpack
🌟 Push the repo to heroku remote
git push heroku master
141. Resources: Buildpack
You can learn more about the buildpack we used in the previous video by following the documentation here
142. Linking Github to Heroku
If you would like to not manually deploy the the app like we have seen in the previous video every time, and you want the app to redeploy anytime you update MASTER in your github repository, then you can set that up through Heroku by following these steps: https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/github-integration
However, since we will be working on the project in the next sections, we recommend that you do not do this so that as you code along, even if your website breaks, your current version of the website is still live on Heroku until you decide to redeploy next.
43. Optional: Git + Heroku commands
🌟 Quick note on how heroku and git works in both local and remote.
144. Optimizing Production Build
🌟 Logger should only be shown in development
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from "redux";
import { persistStore } from "redux-persist";
import logger from "redux-logger";
import rootReducer from "./root-reducer";
const middlewares = [];if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "development") { middlewares.push(logger);}
export const store = createStore(rootReducer, applyMiddleware(...middlewares));
export const persistor = persistStore(store);Section 15: Master Project: CSS in JS- styled-components
145. CSS in JS
🌟 Quick intro to styled components and what it help us to solve & improve
146. styled-components
🌟 Quick intro to styled components with a demo code
147. styled-components In Our App
🌟 Updated two components to use Styled Components
npm i -S styled-components
148. Thinking About Trade-offs

149. styled-components In Our App 2
import React from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { createStructuredSelector } from "reselect";
import { auth } from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
import CartIcon from "../cart-icon/cart-icon.component";
import CartDropDown from "../cart-dropdown/cart-dropdown.component";
import { selectCurrentUser } from "../../redux/user/user.selectors";
import { selectCartHidden } from "../../redux/cart/cart.selectors";
import {
HeaderContainer,
LogoContainer,
OptionsContainer,
OptionLink
} from "./header.styles";
import { ReactComponent as Logo } from "../../assets/crown.svg";
const Header = ({ currentUser, hidden }) => (
<HeaderContainer>
<LogoContainer to="/">
<Logo className="logo" />
</LogoContainer>
<OptionsContainer>
<OptionLink to="/shop">SHOP</OptionLink>
<OptionLink to="/shop">CONTACT</OptionLink>
{currentUser ? (
<OptionLink as="div" onClick={() => auth.signOut()}> SIGN OUT
</OptionLink>
) : (
<OptionLink to="/signin">SIGN IN</OptionLink>
)}
<CartIcon />
</OptionsContainer>
{hidden ? null : <CartDropDown />}
</HeaderContainer>
);
const mapStatetoProps = createStructuredSelector({
currentUser: selectCurrentUser,
hidden: selectCartHidden
});
export default connect(mapStatetoProps)(Header);150. styled-components In Our App 3
🌟 Updated difficult components styles using Styled Components
151. Exercise: styled-components
🌟 Updated the project to use Styled Components completely
Section 16: Master Project:Advanced Redux + Firebase
🌟 Get titles for Section 16
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);152. Section Overview
🌟 Quick intro on what we are going to solve in this section
153. Quick Note: Firebase
Over the next couple of videos we are going to be covering some specific Firebase commands. Keep in mind that as a React Developer, you do not need to memorize these things and most of the time you can always refer to the firebase documentation for more information. We decided to include the process in the course so that you get a clear picture into what is involved in creating a full scale application.
If for some reason you get overwhelmed with Firestore, just keep going and use our provided code since this is not the “important” part of the course.
154. Firebase Refresher
🌟 Quick intro to previously taught Firebase Concepts

155. Firebase Refresher 2
🌟 Quick intro to previously taught Firebase Concepts 2

156. Moving Our Shop Data To Firebase
src/firebase/firebase.util.js
import firebase from "firebase/app";
import "firebase/firestore";
import "firebase/auth";
const config = {
apiKey: "AIzaSyB5bIa1E55zDzEYnRe0zsw7kXxejifBsy0",
authDomain: "crown-clothing-db-ec57f.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://crown-clothing-db-ec57f.firebaseio.com",
projectId: "crown-clothing-db-ec57f",
storageBucket: "",
messagingSenderId: "137189619024",
appId: "1:137189619024:web:1216d928d5eafe8b"
};
firebase.initializeApp(config);
export const createUserProfileDocument = async (userAuth, additionalData) => {
if (!userAuth) return;
const userRef = firestore.doc(`users/${userAuth.uid}`);
const snapshot = await userRef.get();
if (!snapshot.exists) {
const { displayName, email } = userAuth;
const createdAt = new Date();
try {
await userRef.set({ displayName, email, createdAt, ...additionalData });
} catch (error) {
console.log("Error creating users", error.message);
}
}
return userRef;
};
export const addCollectionAndDocuments = (collectionKey, objectsToAdd) => { const collectionRef = firestore.collection(collectionKey); console.log(collectionRef);};
export const auth = firebase.auth();
export const firestore = firebase.firestore();
const provider = new firebase.auth.GoogleAuthProvider();
provider.setCustomParameters({ prompt: "select_account" });
export const signInWithGoogle = () => auth.signInWithPopup(provider);
export default firebase;157. Moving Our Shop Data To Firebase 2
src/firebase/firebase.util.js
import firebase from "firebase/app";
import "firebase/firestore";
import "firebase/auth";
const config = {
apiKey: "AIzaSyB5bIa1E55zDzEYnRe0zsw7kXxejifBsy0",
authDomain: "crown-clothing-db-ec57f.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://crown-clothing-db-ec57f.firebaseio.com",
projectId: "crown-clothing-db-ec57f",
storageBucket: "",
messagingSenderId: "137189619024",
appId: "1:137189619024:web:1216d928d5eafe8b"
};
firebase.initializeApp(config);
export const createUserProfileDocument = async (userAuth, additionalData) => {
if (!userAuth) return;
const userRef = firestore.doc(`users/${userAuth.uid}`);
const snapshot = await userRef.get();
if (!snapshot.exists) {
const { displayName, email } = userAuth;
const createdAt = new Date();
try {
await userRef.set({ displayName, email, createdAt, ...additionalData });
} catch (error) {
console.log("Error creating users", error.message);
}
}
return userRef;
};
export const addCollectionAndDocuments = async ( collectionKey, objectsToAdd) => { const collectionRef = firestore.collection(collectionKey); const batch = firestore.batch(); objectsToAdd.forEach(obj => { const newDocRef = collectionRef.doc(); batch.set(newDocRef, obj); }); await batch.commit();};
export const auth = firebase.auth();
export const firestore = firebase.firestore();
const provider = new firebase.auth.GoogleAuthProvider();
provider.setCustomParameters({ prompt: "select_account" });
export const signInWithGoogle = () => auth.signInWithPopup(provider);
export default firebase;158. Reviewing What We Have Done
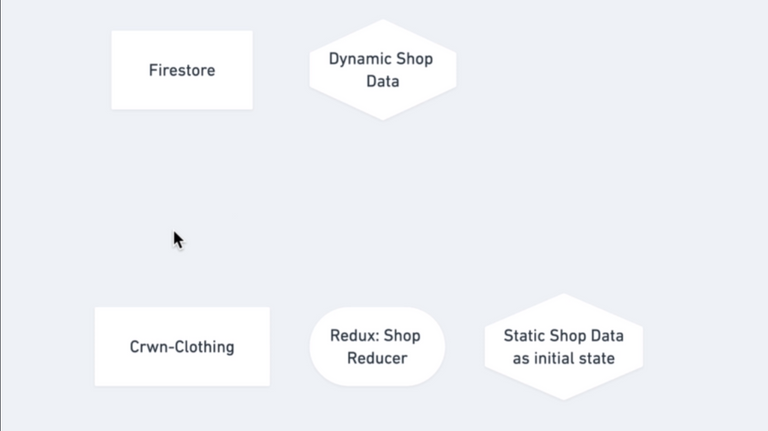
159. Bringing Shop Data To Our App
src/firebase/firebase.utils.js
import firebase from "firebase/app";
import "firebase/firestore";
import "firebase/auth";
const config = {
apiKey: "AIzaSyB5bIa1E55zDzEYnRe0zsw7kXxejifBsy0",
authDomain: "crown-clothing-db-ec57f.firebaseapp.com",
databaseURL: "https://crown-clothing-db-ec57f.firebaseio.com",
projectId: "crown-clothing-db-ec57f",
storageBucket: "",
messagingSenderId: "137189619024",
appId: "1:137189619024:web:1216d928d5eafe8b"
};
firebase.initializeApp(config);
export const createUserProfileDocument = async (userAuth, additionalData) => {
if (!userAuth) return;
const userRef = firestore.doc(`users/${userAuth.uid}`);
const snapshot = await userRef.get();
if (!snapshot.exists) {
const { displayName, email } = userAuth;
const createdAt = new Date();
try {
await userRef.set({ displayName, email, createdAt, ...additionalData });
} catch (error) {
console.log("Error creating users", error.message);
}
}
return userRef;
};
export const addCollectionAndDocuments = async (
collectionKey,
objectsToAdd
) => {
const collectionRef = firestore.collection(collectionKey);
const batch = firestore.batch();
objectsToAdd.forEach(obj => {
const newDocRef = collectionRef.doc();
batch.set(newDocRef, obj);
});
await batch.commit();
};
export const convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap = collections => { const transformedCollection = collections.docs.map(doc => { const { title, items } = doc.data(); return { routeName: encodeURI(title.toLowerCase()), id: doc.id, title, items }; }); console.log(transformedCollection);};
export const auth = firebase.auth();
export const firestore = firebase.firestore();
const provider = new firebase.auth.GoogleAuthProvider();
provider.setCustomParameters({ prompt: "select_account" });
export const signInWithGoogle = () => auth.signInWithPopup(provider);
export default firebase;160. Adding Shop Data To Redux
🌟 Updated the shop data with firestore in Redux
Section 17: Master Project: HOC Patterns
161. WithSpinner HOC
src/components/with-spinner/with-spinner.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import { SpinnerContainer, SpinnerOverlay } from "./with-spinner.styles";
const WithSpinner = WrapperComponent => ({ isLoading, ...props }) => {
return isLoading ? (
<SpinnerOverlay>
<SpinnerContainer />
</SpinnerOverlay>
) : (
<WrapperComponent {...props} />
);
};
export default WithSpinner;162. WithSpinner HOC 2
🌟 Added Loading Spinner for our App
src/pages/shop/shop.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import { Route } from "react-router-dom";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { updateCollections } from "../../redux/shop/shop.actions";
import {
firestore,
convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap
} from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
import CollectionPage from "../collection/collection.component";
import WithSpinner from "../../components/with-spinner/with-spinner.component";import CollectionsOverview from "../../components/collections-overview/collections-overview.components";
const CollectionPageWithSpinner = WithSpinner(CollectionPage);const CollectionsOverviewWithSpinner = WithSpinner(CollectionsOverview);
class ShopPage extends React.Component {
state = { loading: true };
unsubscripbeFromSnapshot = null;
componentDidMount() {
const { updateCollections } = this.props;
const collectionRef = firestore.collection("collections");
this.unsubscripbeFromSnapshot = collectionRef.onSnapshot(snapshot => {
const collectionsMap = convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap(snapshot);
updateCollections(collectionsMap);
this.setState({ loading: false }); });
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unsubscripbeFromSnapshot = null;
}
render() {
const { match } = this.props;
const { loading } = this.state; return (
<div className="shop-page">
<Route
exact
path={`${match.path}`}
render={props => ( <CollectionsOverviewWithSpinner isLoading={loading} {...props} /> )} />
<Route
exact
path={`${match.path}/:collectionId`}
render={props => ( <CollectionPageWithSpinner isLoading={loading} {...props} /> )} />
</div>
);
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
updateCollections: collectionsMap =>
dispatch(updateCollections(collectionsMap))
});
export default connect(
null,
mapDispatchToProps
)(ShopPage);163. Quick Note About Next Lesson
If you are still finding it difficult understanding how Higher Order Components can be useful, you have an optional video next which we explain in higher detail when HOCs are useful and how we can build them ourselves. Enjoy!
164. Optional: How To Build HOCs
Section 18: Master Project: Asynchronous Redux
165. Observables + Observer Pattern
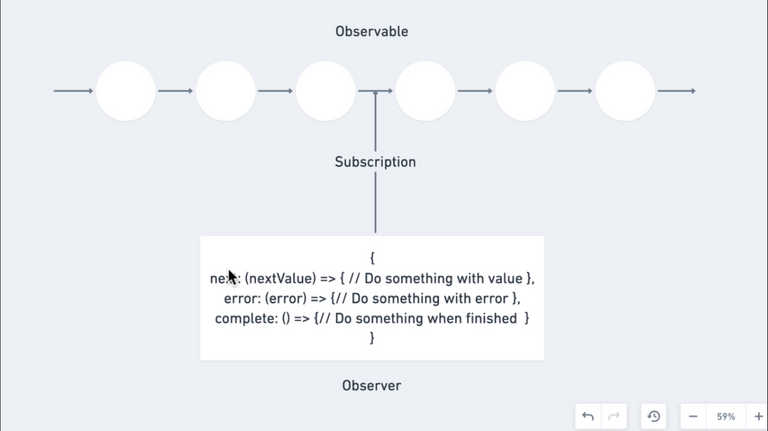
166. Promise Pattern
src/pages/shop/shop.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import { Route } from "react-router-dom";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { updateCollections } from "../../redux/shop/shop.actions";
import {
firestore,
convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap
} from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
import CollectionPage from "../collection/collection.component";
import WithSpinner from "../../components/with-spinner/with-spinner.component";
import CollectionsOverview from "../../components/collections-overview/collections-overview.components";
const CollectionPageWithSpinner = WithSpinner(CollectionPage);
const CollectionsOverviewWithSpinner = WithSpinner(CollectionsOverview);
class ShopPage extends React.Component {
state = {
loading: true
};
componentDidMount() {
const { updateCollections } = this.props;
const collectionRef = firestore.collection("collections");
collectionRef.get().then(snapshot => { const collectionsMap = convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap(snapshot);
updateCollections(collectionsMap);
this.setState({ loading: false });
});
}
render() {
const { match } = this.props;
const { loading } = this.state;
return (
<div className="shop-page">
<Route
exact
path={`${match.path}`}
render={props => (
<CollectionsOverviewWithSpinner isLoading={loading} {...props} />
)}
/>
<Route
exact
path={`${match.path}/:collectionId`}
render={props => (
<CollectionPageWithSpinner isLoading={loading} {...props} />
)}
/>
</div>
);
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
updateCollections: collectionsMap =>
dispatch(updateCollections(collectionsMap))
});
export default connect(
null,
mapDispatchToProps
)(ShopPage);167. Redux Thunk
🌟 Used Redux Thunk to asynchronously fetch data from firestore and save it in Redux
168. What Does Redux Thunk Do
🌟 Redux Thunk explanation by Andrei
169. Debugging Our Code
🌟 Fixed the collections fetching error in CollectionsPage Component
Section 19: Master Project:Container Pattern
170. Container Pattern
src/pages/collection/collection.container.jsx
import { compose } from "redux";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { createStructuredSelector } from "reselect";
import CollectionPage from "./collection.component";
import WithSpinner from "../../components/with-spinner/with-spinner.component";
import { selectIsCollectionsLoaded } from "../../redux/shop/shop.selectors";
const mapStateToProps = createStructuredSelector({
isLoading: state => !selectIsCollectionsLoaded(state)
});
const CollectionPageContainer = compose(
connect(mapStateToProps),
WithSpinner
)(CollectionPage);
export default CollectionPageContainer;171. Refactoring Is A Trade off

Section 20: Master Project:Redux-Saga
🌟 Get titles for Section 20
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);172. Introduction to Sagas
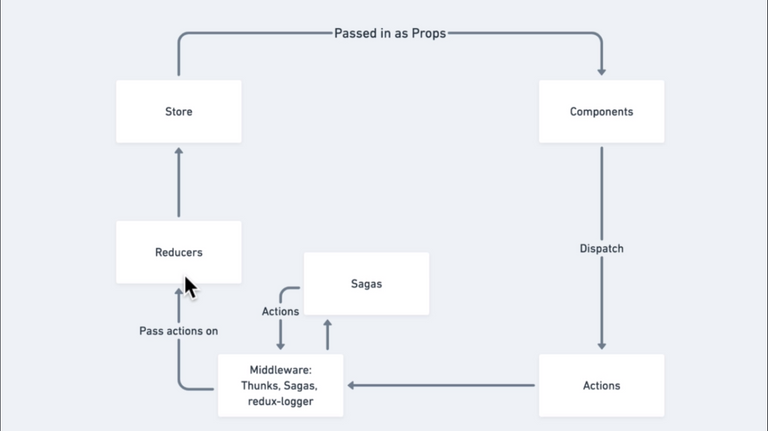
173. Generator Functions
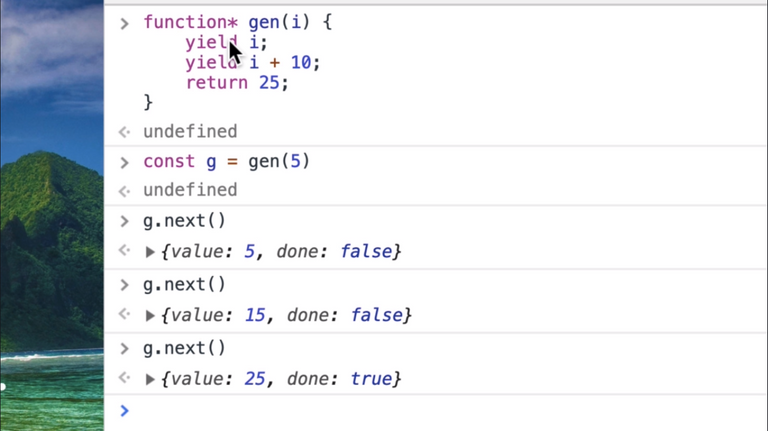
174. Quick Note About Sagas
These next few videos are going to be tough. Keep in mind that getting redux-sagas in one go is usually impossible and it is something you practice multiple times to fully understand. We highly recommend you code along in this section and pause or rewatch the videos whenever you feel unsure of something. Another option is to watch this section all the way through, then come back the 2nd time around and code along once you have a general idea of the concepts.
Good luck!
175. redux-saga
src/redux/shop/shop.sagas.js
import { takeEvery } from "redux-saga/effects";
import { ShopActionTypes } from "./shop.types";
export function* fetchCollectionAsync() {
yield console.log("I am fired");
}
export function* fetchCollectionsStart() {
console.log("1");
yield takeEvery(
ShopActionTypes.FETCH_COLLECTIONS_START,
fetchCollectionAsync
);
}176. Redux Thunk Into Saga
src/redux/shop/shop.sagas.js
import { takeEvery, call, put } from "redux-saga/effects";
import { ShopActionTypes } from "./shop.types";
import {
fetchCollectionsSuccess,
fetchCollectionsFailure
} from "./shop.actions";
import {
firestore,
convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap
} from "../../firebase/firebase.utils";
export function* fetchCollectionAsync() { yield console.log("I am fired"); try { const collectionRef = firestore.collection("collections"); const snapshot = yield collectionRef.get(); const collectionsMap = yield call( convertCollectionsSnapshotToMap, snapshot ); yield put(fetchCollectionsSuccess(collectionsMap)); } catch (error) { yield put(fetchCollectionsFailure(error.message)); }}
export function* fetchCollectionsStart() {
console.log("1");
yield takeEvery(
ShopActionTypes.FETCH_COLLECTIONS_START,
fetchCollectionAsync
);
}177. take(), takeEvery(), takeLatest()
🌟 Deep explanation on take(), takeEvery(), takeLatest()
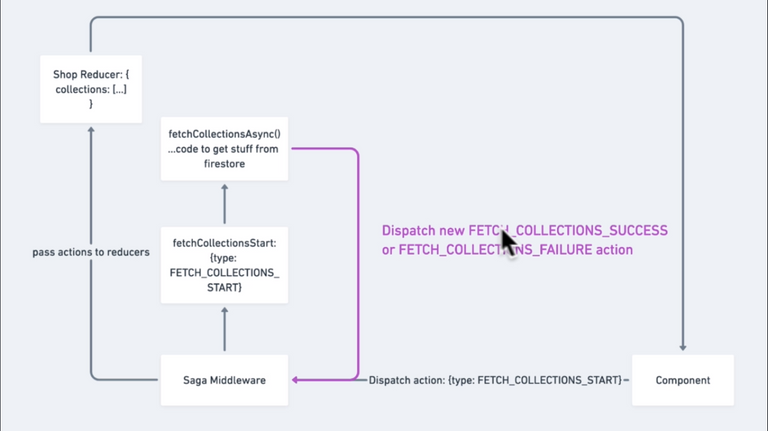
178. Root Saga
src/redux/root-saga.js
import { all, call } from "redux-saga/effects";
import { fetchCollectionsStart } from "./shop/shop.sagas";
export default function* rootSaga() {
yield all([call(fetchCollectionsStart)]);
}179. Planning Ahead With Sagas
🌟 Plan to shift our Users Auth calls into Redux Saga
180. Google Sign In Into Sagas
🌟 Implemented Google Sign In Into Sagas
181. Email Sign In Into Sagas
🌟 Implemented Email Sign In Into Sagas
182. Reviewing Our Sagas
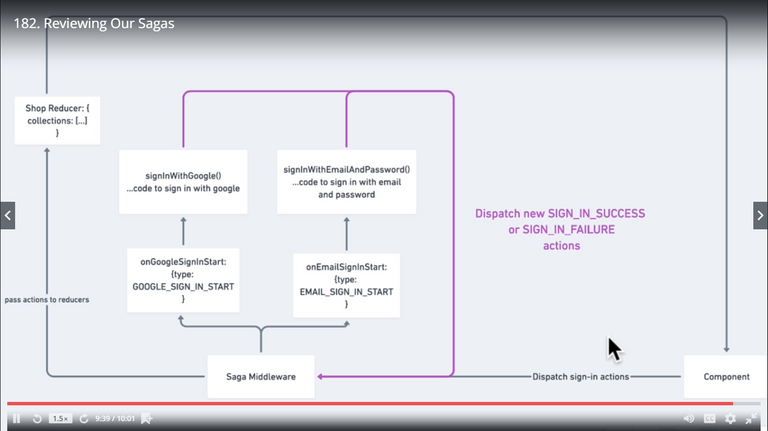
183. Recreating Persistence
🌟 Implemented User persistence recreation
184. Sign Out With Sagas
🌟 Implemented User persistence recreation
185. Clear Cart Saga
🌟 Implemented Clear Cart Saga on Sign out
186. Solution: Sign Up Saga
🌟 Implemented Sign Up Saga
Section 21: Master Project: ReactHooks
🌟 Get titles for Section 21
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);187. React Hooks Introduction(useState)
🌟 Intro to useState hook
188. Why Did React Add Hooks
If you want to learn more about why the React team decided to add Hooks to the library, you can find the motivation behind their decision right from their mouth https://reactjs.org/docs/hooks-intro.html#motivation
189. useEffect
useEffect || JSON Placeholder || useEffect Example
190. Hook Rules
🌟 Hooks cannot be conditionally renders in top level. Conditions should be inside the Hooks
191. Converting ClassComponents With useState
🌟 Converted SignIn Component and SignUp Component to use the State hook
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import {
googleSignInStart,
emailSignInStart
} from "../../redux/user/user.actions";
import FormInput from "../form-input/form-input.components";
import CustomButton from "../custom-button/custom-button.component";
import {
SignInContainer,
SignInTitle,
ButtonsBarContainer
} from "./sign-in.styles";
const SignIn = ({ emailSignInStart, googleSignInStart }) => {
const [UserCredentials, setCredentials] = useState({
email: "",
password: ""
});
const { email, password } = UserCredentials;
const handleSubmit = async e => {
e.preventDefault();
emailSignInStart(email, password);
};
const handleChange = e => {
const { value, name } = e.target;
setCredentials({ ...UserCredentials, [name]: value });
};
return (
<SignInContainer>
<SignInTitle>I already have an account</SignInTitle>
<span>Sign in with you email and password</span>
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<FormInput
type="email"
name="email"
value={email}
handleChange={handleChange}
label="Email"
required
/>
<FormInput
type="password"
name="password"
value={password}
handleChange={handleChange}
label="Password"
required
/>
<ButtonsBarContainer>
<CustomButton type="submit">Sign In</CustomButton>
<CustomButton
type="button"
onClick={googleSignInStart}
isGoogleSignIn
>
Sign in with Google
</CustomButton>
</ButtonsBarContainer>
</form>
</SignInContainer>
);
};
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
googleSignInStart: () => dispatch(googleSignInStart()),
emailSignInStart: (email, password) =>
dispatch(emailSignInStart({ email, password }))
});
export default connect(
null,
mapDispatchToProps
)(SignIn);192. useEffect In Our App
🌟 Converted some Component to use useEffect hook
193. useEffect as ComponentWillUnmount()
🌟 useEffect hook clean up function acts as a ComponentWillUnmount
194. useEffect Cheat Sheet
A quick recap of what we have learned about useEffect:
🌟 ComponentDidMount
//Class
componentDidMount() {
console.log('I just mounted!');
}
//Hooks
useEffect(() => {
console.log('I just mounted!');
}, [])🌟 ComponentWillUnmount
//Class
componentWillUnmount() {
console.log('I am unmounting');
}
//Hooks
useEffect(() => {
return () => console.log('I am unmounting');
}, [])🌟 ComponentWillReceiveProps
//Class
componentWillReceiveProps(nextProps) {
if (nextProps.count !== this.props.count) {
console.log('count changed', nextProps.count);
}
}
//Hooks
useEffect(() => {
console.log('count changed', props.count);
}, [props.count])195. Custom Hooks
196. Custom Hooks 2
🌟 Learned more about useEffect()
197. useReducer
useReducer || useReducer example
198. useContext + useMemo + useCallback
There are a few other Hooks we still need to talk about such as useContext or useMemo or useCallback However, we are covering topics like these in later sections in the course when we learn a little bit more about things like ContextAPI and Performance.
So hang on tight and you will learn about them shortly as we will continue to use hooks throughout the upcoming sections!
Section 22: Master Project: Stripe Payments Part 2 - Back end
🌟 Get titles for Section 22
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);199. About This Section
In order to have a fully functioning e commerce project with payments, we need to create a backend server for our Stripe payments. This section coming up does not talk about React, but instead, allows you to have a fully functioning application because our goal here is to have a project as complete as possible for you. However, this is not an important part of the course, so if you do not want to learn about the backend, you can skip this section, or you can just grab the code that we will provide in the last lecture of this section. The only thing you will be missing out on is the full ability to accept payments with Stripe (since currently the payment info the user sends on the frontend isn’t doing anything).
Remember, this section is completely optional!
200. Introduction To Backend
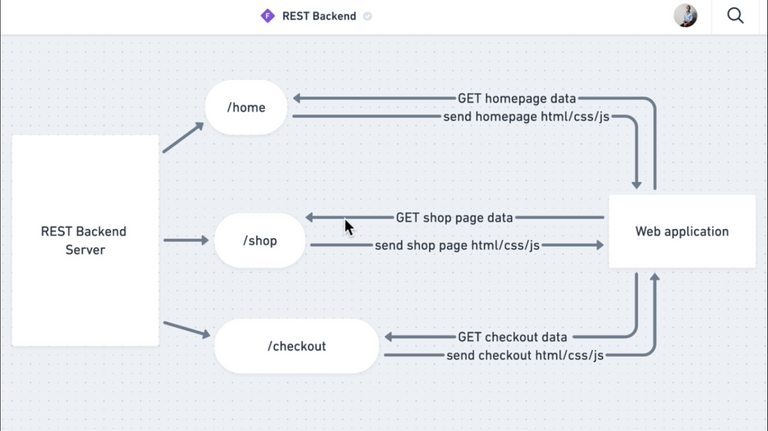
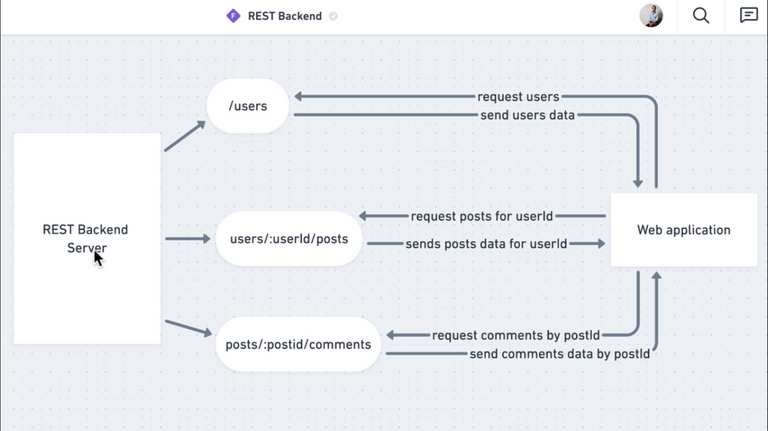
201. Cloning From This Point On
If you do choose to skip this section and just fork and clone this repo, or any repo from this point on in the course, remember to add a file called .env to the root folder! In that .env file remember to add a STRIPE_SECRET_KEY value equal to your own secret key from your stripe dashboard. You can find it in the same place where you found your publishable key in the developers tab under api keys. You will have to enter the password in to reveal it!
You will also need to connect your existing Heroku app to this new forked and cloned repo, or you have to create a new Heroku app and push to it. A quick refresher on how to do either of these:
🌟 Set to an existing Heroku app
To set to an existing Heroku app you already have deployed, you need to know the name of the app you want to deploy to. To see a list of all the apps you currently have on Heroku:
heroku appsCopy the name of the app you want to connect the project to, then run:
heroku git:remote -a <PASTE_YOUR_APP_NAME_HERE>And now you’ll have your repo connected to the heroku app under the git remote name heroku.
If the Heroku app you connected was deploying just a create-react-app project from earlier in the lesson, you will need to remove the mars/create-react-app-buildpack buildpack first. You can check if you have this buildpack by running:
heroku buildpacksWhich will list any buildpacks you currently have, if you see mars/create-react-app-buildpack in the list, you can remove it by running:
heroku buildpacks:remove mars/create-react-app-buildpack
Then skip to the bottom of this article to see what to do next!
🌟 To create a new Heroku app
Create a new Heroku project by typing in your terminal:
heroku createThis will create a new Heroku project for you. Then run:
git remote -vYou should see heroku https://git.heroku.com/<RANDOMLY_GENERATED_NAME_OF_YOUR_APP> in the list. This means you have successfully connected your project to the newly created Heroku app under the git remote of heroku.
🌟 Deploying to Heroku
Before we deploy, you also need to set a config variable of STRIPE_SECRET_KEY to the same secret key value from your stripe dashboard, the same one in your .env file. The .env file is only for local development, in order for our heroku production app to have access to this secret key, we add it to our Heroku projects config variables by typing:
heroku config:set STRIPE_SECRET_KEY=<YOUR_STRIPE_SECRET_KEY>After that, you can deploy to heroku by running:
git push heroku masterYou will see this warning message if you are pushing to an existing app:
! [rejected] master -> master (fetch first)
error: failed to push some refs to 'https://git.heroku.com/<YOUR_HEROKU_APP_NAME>'
hint: Updates were rejected because the remote contains work that you do
hint: not have locally. This is usually caused by another repository pushing
hint: to the same ref. You may want to first integrate the remote changes
hint: (e.g., 'git pull ...') before pushing again.
hint: See the 'Note about fast-forwards' in 'git push --help' for details.This is because we are pushing to an existing app that was deploying an entirely different repository from what we have now. Simply run:
git push heroku master --forceThis will overwrite the existing Heroku app with our new code.
🌟 Open our Heroku project
After heroku finishes building our project, we can simply run:
heroku openThis will open up our browser and take us to our newly deployed Heroku project!
202. Creating our Server Inside the Project
🌟 Backend initialized
203. Building A Basic Server
express || dotenv || cors || body-parser
server.js
const express = require("express");
const cors = require("cors");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const path = require("path");
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") require("dotenv").config();
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 8081;
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(cors());
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, "client/build")));
app.get("*", (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "client/build", "index.html"));
});
}
app.listen(port, error => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log(`Server running on port ${port}`);
});204. What We Are Building
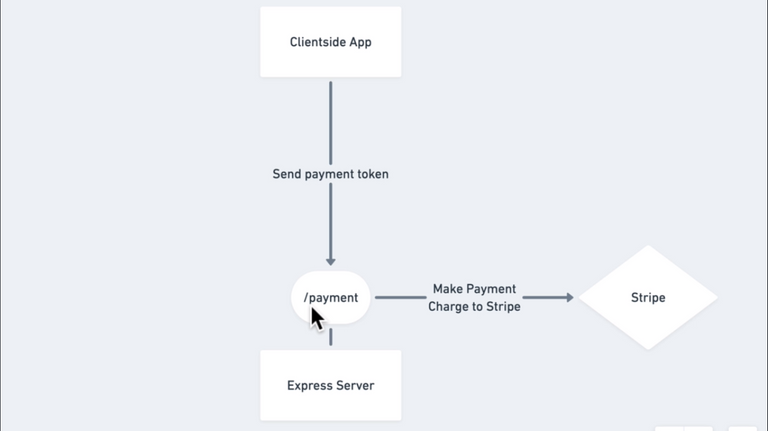
205. Backend Payment Route
const express = require("express");
const cors = require("cors");
const bodyParser = require("body-parser");
const path = require("path");
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== "production") require("dotenv").config();
const stripe = require("stripe")(process.env.STRIPE_SECRET_KEY);
const app = express();
const port = process.env.PORT || 8081;
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: true }));
app.use(cors());
if (process.env.NODE_ENV === "production") {
app.use(express.static(path.join(__dirname, "client/build")));
app.get("*", (req, res) => {
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, "client/build", "index.html"));
});
}
app.post("/payment", (req, res) => { console.log(req.body); const { token: { id }, amount } = req.body; console.log(id); console.log(amount); const body = { source: req.body.token.id, amount: req.body.amount, curreny: "usd" }; stripe.charges.create(body, (stripeErr, stripeRes) => { if (stripeErr) { res.status(500).send({ error: stripeErr }); } else { res.status(200).send({ success: stripeRes }); } });});
app.listen(port, error => {
if (error) throw error;
console.log(`Server running on port ${port}`);
});206. Connecting Client To Server
client/src/components/stripe-button/stripe-button.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import StripeCheckout from "react-stripe-checkout";
import axios from "axios";
import crown from "../../assets/crown.svg";
const StripeCheckoutButton = ({ price }) => {
const priceForStripe = price * 100;
const publishableKey = "pk_test_2hJtHnCWfCA14ioo1FKhoZMS00tev3ElY9";
const onToken = token => { axios({ url: "payment", method: "post", data: { amount: priceForStripe, token } }) .then(response => { alert("Payment Successful"); }) .catch(error => { console.log(`Payment error: ${error}`); alert( "There was an issue with your payment. Please make sure use the provided credit card" ); }); };
return (
<StripeCheckout
label="Pay Now"
name="Crown Clothing Ltd."
billingAddress
shippingAddress
image={crown}
description={`Your total is $${price}`}
amount={priceForStripe}
panelLabel="Pay Now"
token={onToken}
stripeKey={publishableKey}
/>
);
};
export default StripeCheckoutButton;207. Deploying To Production
Removed the old React build-pack to make the node app deploy successful.
Section 23: Master Project: ContextAPI
🌟 Get titles for Section 23
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);208. Quick note about cloning this repo
🌟 Quick note about cloning this repo
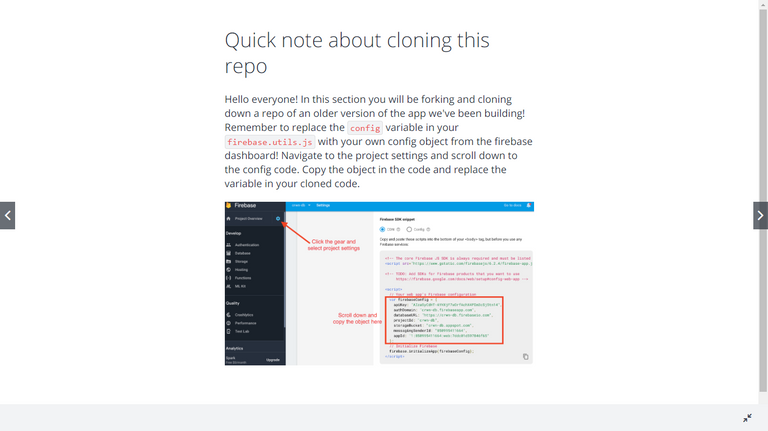
209. Introduction To Context API
Context API Example Start Repo
This section will be taught from the an older commit before the introduction of advanced Redux concepts
210. Context Consumer + useContextHook
src/contexts/collections/collections.context.js
import { createContext } from 'react';
import SHOP_DATA from './shop.data';
const CollectionsContext = createContext(SHOP_DATA);
export default CollectionsContext;src/pages/collection/collection.component.jsx
import React, { useContext } from 'react';
import CollectionItem from '../../components/collection-item/collection-item.component';
import CollectionsContext from '../../contexts/collections/collections.context';
import './collection.styles.scss';
const CollectionPage = ({ match }) => {
const collections = useContext(CollectionsContext); const collection = collections[match.params.collectionId];
const { title, items } = collection;
return (
<div className='collection-page'>
<h2 className='title'>{title}</h2>
<div className='items'>
{items.map(item => (
<CollectionItem key={item.id} item={item} />
))}
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default CollectionPage;211. Context Provider
src/contexts/current-user/current-user.context.js
import { createContext } from 'react';
const CurrentUserContext = createContext(undefined);
export default CurrentUserContext;src/App.js
import React from 'react';
import { Switch, Route, Redirect } from 'react-router-dom';
import './App.css';
import HomePage from './pages/homepage/homepage.component';
import ShopPage from './pages/shop/shop.component';
import SignInAndSignUpPage from './pages/sign-in-and-sign-up/sign-in-and-sign-up.component';
import CheckoutPage from './pages/checkout/checkout.component';
import Header from './components/header/header.component';
import { auth, createUserProfileDocument } from './firebase/firebase.utils';
import CurrentUserContext from './contexts/current-user/current-user.context';
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
currentUser: null
};
}
unsubscribeFromAuth = null;
componentDidMount() {
this.unsubscribeFromAuth = auth.onAuthStateChanged(async userAuth => {
if (userAuth) {
const userRef = await createUserProfileDocument(userAuth);
userRef.onSnapshot(snapShot => {
this.setState({
currentUser: {
id: snapShot.id,
...snapShot.data()
}
});
});
}
this.setState({ currentUser: userAuth });
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unsubscribeFromAuth();
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<CurrentUserContext.Provider value={this.state.currentUser}> <Header /> </CurrentUserContext.Provider> <Switch>
<Route exact path='/' component={HomePage} />
<Route path='/shop' component={ShopPage} />
<Route exact path='/checkout' component={CheckoutPage} />
<Route
exact
path='/signin'
render={() =>
this.state.currentUser ? (
<Redirect to='/' />
) : (
<SignInAndSignUpPage />
)
}
/>
</Switch>
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;src/components/header/header.component.jsx
import React, { useContext, useState } from 'react';import { Link } from 'react-router-dom';
import { auth } from '../../firebase/firebase.utils';
import CartIcon from '../cart-icon/cart-icon.component';
import CartDropdown from '../cart-dropdown/cart-dropdown.component';
import CurrentUserContext from '../../contexts/current-user/current-user.context';
import { CartContext } from '../../providers/cart/cart.provider';
import { ReactComponent as Logo } from '../../assets/crown.svg';
import './header.styles.scss';
const Header = () => {
const currentUser = useContext(CurrentUserContext); const { hidden } = useContext(CartContext);
return (
<div className='header'>
<Link className='logo-container' to='/'>
<Logo className='logo' />
</Link>
<div className='options'>
<Link className='option' to='/shop'>
SHOP
</Link>
<Link className='option' to='/shop'>
CONTACT
</Link>
{currentUser ? (
<div className='option' onClick={() => auth.signOut()}>
SIGN OUT
</div>
) : (
<Link className='option' to='/signin'>
SIGN IN
</Link>
)}
<CartIcon />
</div>
{hidden ? null : <CartDropdown />}
</div>
);
};
export default Header;212. Cart Context
🌟 Created a Cart Context to leverage the hidden value for the cart dropdown
213. Provider Context Pattern
214. Provider Context Pattern 2
Context API Provider Example Complete
src/providers/cart/cart.provider.jsx
import React, { createContext, useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import {
addItemToCart,
removeItemFromCart,
filterItemFromCart,
getCartItemsCount,
getCartTotal
} from './cart.utils';
export const CartContext = createContext({
hidden: true,
toggleHidden: () => {},
cartItems: [],
addItem: () => {},
removeItem: () => {},
clearItemFromCart: () => {},
cartItemsCount: 0,
cartTotal: 0
});
const CartProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [hidden, setHidden] = useState(true);
const [cartItems, setCartItems] = useState([]);
const [cartItemsCount, setCartItemsCount] = useState(0);
const [cartTotal, setCartTotal] = useState(0);
const addItem = item => setCartItems(addItemToCart(cartItems, item));
const removeItem = item => setCartItems(removeItemFromCart(cartItems, item));
const toggleHidden = () => setHidden(!hidden);
const clearItemFromCart = item =>
setCartItems(filterItemFromCart(cartItems, item));
useEffect(() => {
setCartItemsCount(getCartItemsCount(cartItems));
setCartTotal(getCartTotal(cartItems));
}, [cartItems]);
return (
<CartContext.Provider
value={{
hidden,
toggleHidden,
cartItems,
addItem,
removeItem,
clearItemFromCart,
cartItemsCount,
cartTotal
}}
>
{children}
</CartContext.Provider>
);
};
export default CartProvider;215. Redux vs Context API
🌟 Brief explanation on when to use Redux and when to use Context API
🌟 Redux-Big Projects & Context API-Small and Medium level Projects
Section 24: Master Project: GraphQL+ Apollo
🌟 Get titles for Section 24
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);216. Introduction To GraphQL
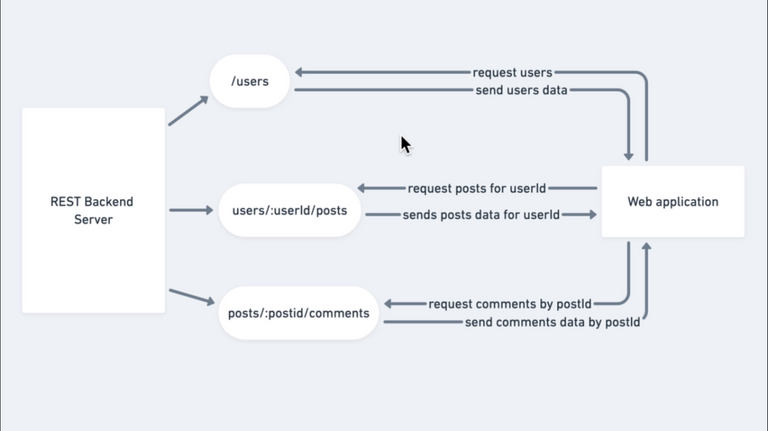
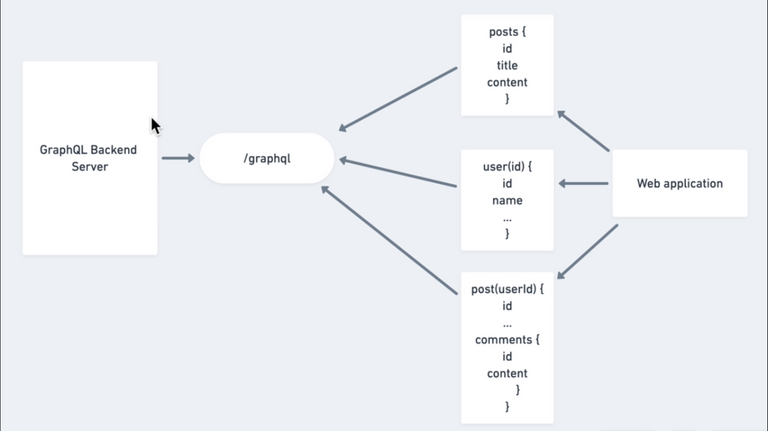
217. Course Guideline + GitHub Links
218. GraphQL Playground
220. GraphQL Playground 2
Crown Clothing GraphQL playground || GraphQL Basic Types || Prisma Server for playground
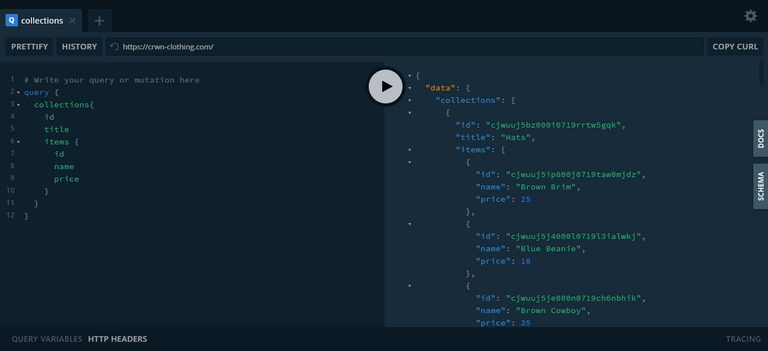
219. Backend Code
When we talk about GraphQL, it usually comes with two components: The frontend part and the backend part. As React developers, we will usually only concern ourselves with the frontend implementation of GraphQL and this is what we will be exploring over the coming videos. However, for those curious on how to best build a GraphQL server, we have provided for you the backend code that we use for this course, as well as the list of some popular options out there for building such a server:
Prisma what we use in the above link Hasura Apollo Server
Quick way to build a GraphQL server: graphql-yoga
A quick step by step guide on how to set up your own GraphQL server
221. Introduction To Apollo
Apollo Client || apollo-boost || react-apollo || graphql-npm
Created own graphql server endpoint to tackle cors errors.
222. Apollo Container
src/components/collections-overview/collections-overview.container.jsx
import React from "react";
import { Query } from "react-apollo";
import { gql } from "apollo-boost";
import CollectionsOverview from "./collections-overview.component";
import Spinner from "../spinner/spinner.component";
const GET_COLLECTIONS = gql`
{
collections {
id
title
items {
id
name
price
imageUrl
}
}
}
`;
const CollectionsOverviewContainer = () => (
<Query query={GET_COLLECTIONS}>
{({ loading, error, data }) => {
if (loading) return <Spinner />;
return <CollectionsOverview collections={data.collections} />;
}}
</Query>
);
export default CollectionsOverviewContainer;223. Query With Variables
src/components/collections-overview/collections-overview.container.jsx
import React from "react";
import { Query } from "react-apollo";
import { gql } from "apollo-boost";
import CollectionPage from "./collection.component";
import Spinner from "../../components/spinner/spinner.component";
const GET_COLLECTION_BY_TITLE = gql`
query getCollectionsByTitle($title: String!) {
getCollectionsByTitle(title: $title) {
id
title
items {
id
name
price
imageUrl
}
}
}
`;
const CollectionPageContainer = ({ match }) => (
<Query
query={GET_COLLECTION_BY_TITLE}
variables={{ title: match.params.collectionId }}
>
{({ loading, data: { getCollectionsByTitle } }) => {
if (loading) return <Spinner />;
return <CollectionPage collection={getCollectionsByTitle} />;
}}
</Query>
);
export default CollectionPageContainer;224. GraphQL vs Redux
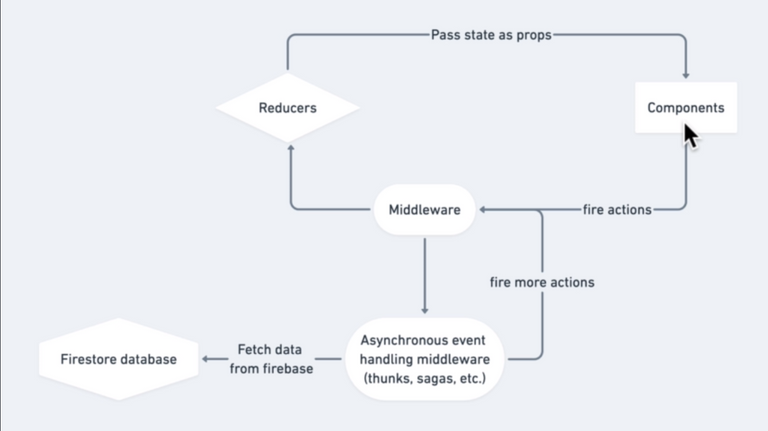

225. Mutations On The Client
227. Mutations On The Client 2
Apollo Cache || Apollo Local Resolver
src/graphql/resolvers.js
import { gql } from "apollo-boost";
export const typeDefs = gql`
extend type Mutation {
ToggleCartHidden: Boolean!
}
`;
const GET_CART_HIDDEN = gql`
{
cartHidden @client
}
`;
export const resolvers = {
Mutation: {
toggleCartHidden: (_root, _args, { cache }) => {
const { cartHidden } = cache.readQuery({
query: GET_CART_HIDDEN
});
cache.writeQuery({
query: GET_CART_HIDDEN,
data: { cartHidden: !cartHidden }
});
return !cartHidden;
}
}
};226. Resources: Mutations
To learn more about mutations, we recommend checking out the Apollo documentation here. Mutations are hard to grasp at first, but as with anything, once you get used to the syntax, it becomes nice and easy!
228. Adding Items With Apollo
229. Adding Items With Apollo 2
🌟 Added cartItems using Apollo
230. Note Compose in next lesson
Hello everyone! In the next lesson, we are going to use a method called compose that we import from 'react-apollo'. Unfortunately with the recent React-Apollo update to v3.0.0 it’s been removed from React-Apollo and is no longer something we can import from this library. Luckily compose was just a copy of lodash’s flowRight. Lodash is just a small library that gives us access to a bunch of helper functions, of which flowRight is one of! In the following lesson, anyplace you see compose just use lodash flowRight!
You can install lodash in your project by adding it as a dependency as follows:
If you’re using yarn:
yarn add lodash
If you’re using npm:
npm install lodash
You can then import flowRight into your file like so:
import { flowRight } from 'lodash';
and just replace any place in the lesson where we use compose with flowRight:
export default compose(
//...code
)(CollectionItemContainer);becomes
export default flowRight(
// ...code
)(CollectionItemContainer);You can find out more about this breaking change here as well: https://github.com/apollographql/react-apollo/issues/3330. So push forward with the lesson :)
231. CartItem Count With Apollo
🌟 Added itemCount back using Apollo
232. Exercises: Adding More GraphQL
As an exercise, attempt to convert the remaining instances of redux in the application over to using our Apollo local cache!
You can find a link to all the code we’ve done up to now here:
https://github.com/ZhangMYihua/graphql-practice
You can also find a full solution repo at this GitHub link to check your solutions:
https://github.com/ZhangMYihua/graphql-practice-complete
233. Should You Use GraphQL
🌟 Tradeoff in using GraphQl over Redux
Section 25: Master Project: Mobile Support
234. Mobile Responsiveness
src/global.styles.js
import { createGlobalStyle } from "styled-components";
export const GlobalStyle = createGlobalStyle`
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
font-family: "Open Sans Condensed", sans-serif;
padding: 20px 60px;
@media screen and (max-width: 800px){
padding: 10px;
}
}
a {
text-decoration: none;
color: black;
}
`;235. Mobile Responsiveness 2
🌟 Responsive design for Mobiles
236. Exercise: Mobile Friendly App
As a bonus exercise for those that want to try, you can continue to play around with our shopping application and customize it to your liking on mobile! Beyond that, from this point forward, you can customize and add any additional features you want in this app. As with any programming project, the opportunities to improve upon it are endless.
The rest of the sections will close out some of the lessons we learned, as well as introduce you to some bonus topics like Testing and PWAs (we will even convert our master project to a PWA so all of these mobile changes we made will now make our app behave like a mobile app), but are only optional for you to take. Enjoy!
Resources for this lecture Github: Code up to now Github: Solution
Section 26: Master Project: React Performance
🌟 Get titles for Section 22
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);237. Code Splitting Introduction
238. Introducing React Lazy
239. React Lazy + Suspense
App.js
import React, { useEffect, lazy, Suspense } from "react";import { Switch, Route, Redirect } from "react-router-dom";
import { connect } from "react-redux";
import { createStructuredSelector } from "reselect";
import Header from "./components/header/header.component";
import Spinner from "./components/spinner/spinner.component";
import { selectCurrentUser } from "./redux/user/user.selectors";
import { checkUserSession } from "./redux/user/user.actions";
import { GlobalStyle } from "./global.styles";
const HomePage = lazy(() => import("./pages/homepage/homepage.component"));const ShopPage = lazy(() => import("./pages/shop/shop.component"));const SignInAndSignUpPage = lazy(() => import("./pages/sign-in-and-sign-up/sign-in-and-sign-up.component"));const CheckoutPage = lazy(() => import("./pages/checkout/checkout.component"));
const App = ({ checkUserSession, currentUser }) => {
useEffect(() => {
checkUserSession();
}, [checkUserSession]);
return (
<div>
<GlobalStyle />
<Header />
<Switch>
<Suspense fallback={<Spinner />}> <Route exact path="/" component={HomePage} />
<Route
exact
path="/signin"
render={() =>
currentUser ? <Redirect to="/" /> : <SignInAndSignUpPage />
}
/>
<Route path="/shop" component={ShopPage} />
<Route exact path="/checkout" component={CheckoutPage} />
</Suspense> </Switch>
</div>
);
};
const mapStateToProps = createStructuredSelector({
currentUser: selectCurrentUser
});
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
checkUserSession: () => dispatch(checkUserSession())
});
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(App);240. Error Boundaries
Error Boundaries || 404 Illustrations
src/components/error-boundary/error-boundary.component.jsx
import React from "react";
import {
ErrorImageOverlay,
ErrorImageContainer,
ErrorImageText
} from "./error-boundary.styles";
class ErrorBoundary extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super();
this.state = {
hasErrored: false
};
}
static getDerivedStateFromError(error) {
// process the error here
return { hasErrored: true };
}
componentDidCatch(error, info) {
console.log(error);
}
render() {
if (this.state.hasErrored) {
return (
<ErrorImageOverlay>
<ErrorImageContainer imageUrl="https://i.imgur.com/A040Lxr.png" />
<ErrorImageText>Sorry This Page is Lost in Space</ErrorImageText>
</ErrorImageOverlay>
);
}
return this.props.children;
}
}
export default ErrorBoundary;241. React.memo, PureComponent,shouldComponentUpdate
React.memo || React.PureComponent || React Dev Tools
242. Performance In Our App
🌟 Learned how to use the Profiler from React Dev tools
243. useCallback
244. useMemo
import React, { useState, useCallback, useMemo } from 'react';
import logo from './logo.svg';
import './App.css';
const App = () => {
const [count1, setCount1] = useState(0);
const [count2, setCount2] = useState(0);
const incrementCount1 = useCallback(() => setCount1(count1 + 1), [count1]);
const incrementCount2 = useCallback(() => setCount2(count2 + 1), [count2]);
const doSomethingComplicated = useMemo(() => {
console.log('I am computing something complex');
return ((count1 * 1000) % 12.4) * 51000 - 4000;
}, [count1]);
return (
<div className='App'>
<header className='App-header'>
<img src={logo} className='App-logo' alt='logo' />
Count1: {count1}
<button onClick={incrementCount1}>Increase Count1</button>
Count2: {count2}
<button onClick={incrementCount2}>Increase Count2</button>
complexValue: {doSomethingComplicated}
</header>
</div>
);
};
export default App;245. Gzipping and Compression
🌟 Build Files Size
File sizes after gzip:
remote: 225.01 KB build/static/js/2.16332b27.chunk.js
remote: 7.71 KB build/static/js/main.1424a885.chunk.js
remote: 7.21 KB build/static/js/3.941ee3f8.chunk.js
remote: 2.15 KB build/static/js/9.54c4bca4.chunk.js
remote: 1.57 KB build/static/js/6.2b158ef5.chunk.js
remote: 1.48 KB build/static/js/4.ff8f2bb2.chunk.js
remote: 1.36 KB build/static/js/5.7b8abb52.chunk.js
remote: 1.23 KB build/static/js/runtime~main.09f6eda3.js
remote: 1.09 KB build/static/js/7.8eac9c54.chunk.js
remote: 451 B build/static/js/8.79499474.chunk.js
remote: 277 B build/static/css/main.795991f2.chunk.cssSection 27: React Interview Questions + Advice
246. Don’t Overcomplicate

247. Be A Late Follower

248. Break Things Down

249. It Will Never Be Perfect
250. Learning Guideline
Since I get this question a lot, I’ve added an info graph to help you decide what skills you should focus on and what you need to learn to succeed as a programmer.
251. Endorsements On LinkedIn
If you are looking to create a LinkedIn profile or you already have one, you can join our LinkedIn group here. This group is meant for you to increase your LinkedIn connections, meet other coders, and also endorse each other’s skills.
You can join the group here and then go ahead and endorse some of the member’s skills (other people will do the same for you as they join).
If you have any questions, reach out in our private Discord chat community in the #job-hunting channel!
252. Become An Alumni
I have created the #alumni channel on Discord as well as the Alumni role so you can network with other graduates. Please let myself or the management team know that you have finished the course so you can get the alumni badge in the community! Simply post your completion certificate in the #alumni channel and tag the @Management Team. If you have finished the course I highly recommend you join the channel and stay up to date and network throughout your career. You never know how it may come in handy in the future.
It would be great to have the alumni follow up on their career journey such as: Did they find a new job? or Did they enroll in some further study? or even Did they launch their own business/product?
Many students would benefit from this and I hope you give back a bit to the community :)
253. Common React InterviewQuestions
Section 28: Bonus: Progressive Web App
254. Note About This Section
This upcoming section is all about PWAs and part of it is from Andrei’s course The Complete Junior to Senior Web Developer Roadmap. HOWEVER, Yihua will come in at the end and actually demonstrate how to implement our app from this course as a Progressive Web App. If you already know about PWAs, then you can go straight to the Converting Our App To PWA lesson!
Enjoy :)
255. Progressive Web Apps
🌟 Short intro on PWA

256. Resources: Progressive Web Apps
In case you want further reading on Progressive Web Apps:
Submitting PWA to 3 app stores
Finally, here is the link to the robofriends-redux github repository which I will be referencing in the next couple of videos which is very similar to our Monsters Rolodex App we built in this course.
Ps You can explore some of the top PWAs from around the world: https://appsco.pe/
257. Progressive Web Apps Examples

258. PWA - HTTPS
🌟 Short intro on PWA HTTPS
259. Resources: PWA - HTTPS
First, in case you have never put a website online using Github Pages, you can use this tutorial to have your Github website up and running in 5 minutes: GitHub Pages Please note that this is only for simple websites. If you want to have github pages work with create react app, we cover this in the upcoming video: Deploying Our React App
Progressive Web Apps Checklist: PWA Checklist
Finally, if you would like to implement HTTPS yourself, I recommend you use Let’s Encrypt
260. PWA - App Manifest
{
"short_name": "React App",
"name": "Create React App Sample",
"icons": [
{
"src": "favicon.ico",
"sizes": "64x64 32x32 24x24 16x16",
"type": "image/x-icon"
}
],
"start_url": ".",
"display": "standalone",
"theme_color": "#000000",
"background_color": "#ffffff"
}261. PWA - Service Workers
262. Resources: PWA - Service Workers
Service Worker is implemented very easily into a react based project. You can see this Git Diff to see what you would need to do to add service worker into an existing create react app project without the default service worker.
For further information on the topics covered in the previous video:
More information on push notifications for those who want to see how it is implemented
263. PWA - Final Thoughts
🌟 Final thoughts on when and where to use the PWA
264. Converting Our App To PWA
Express-sslify || Lighthouse Chrome Extension || crwn-clothing EndGame
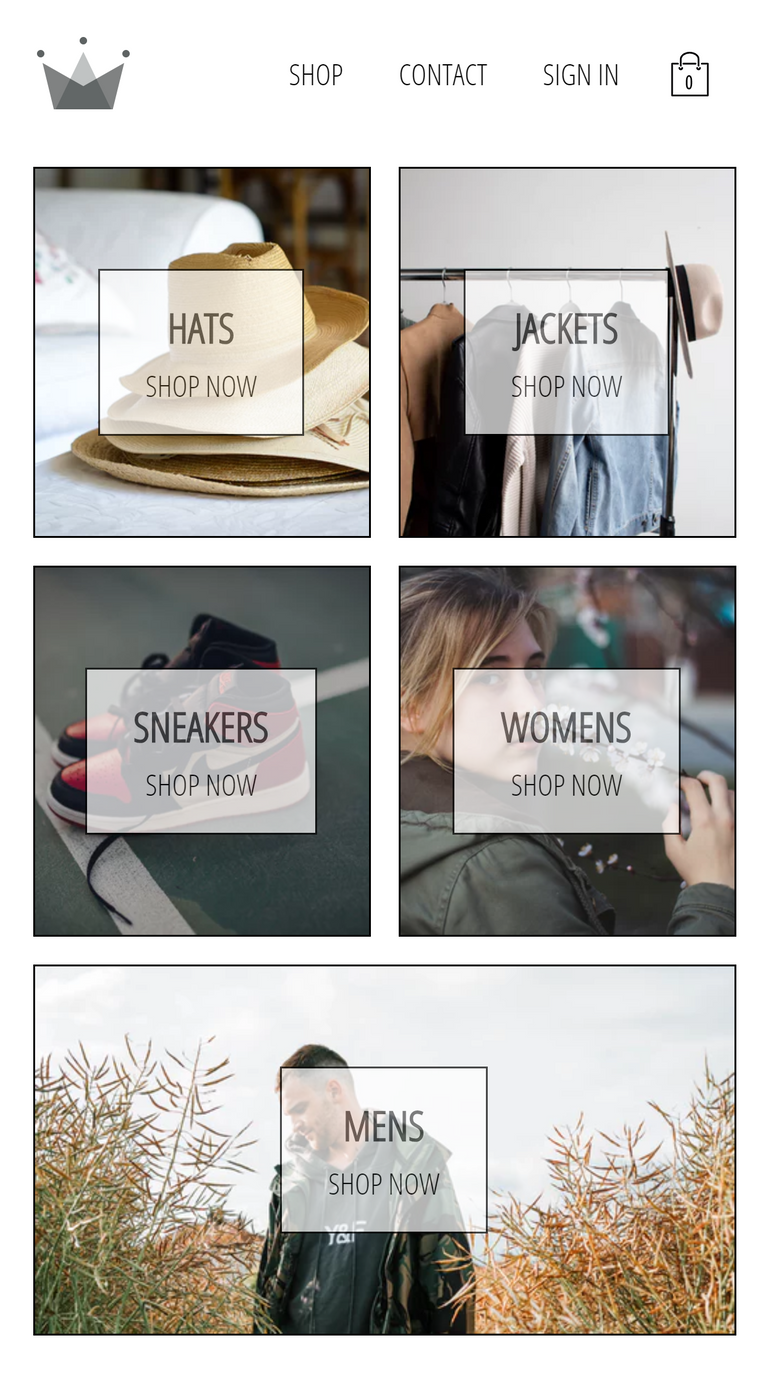
Section 29: Bonus: Testing
🌟 Get titles for Section 29
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(
title => title.textContent
);265. Note About This Section
This upcoming section is all about testing and it is from Andrei’s course The Complete Junior to Senior Web Developer Roadmap. Although this isn’t a required part of this course, testing is something that will be important in your career so I have decided to include it on here. If you are new to testing, then you can watch all of the videos. If you know about testing and only want to focus on React specific testing, you can start from halfway at the lesson titled Note: Testing React Apps and watch from there. If you already know everything about testing and you just want to see how tests are implemented in our Master Project, go straight to Testing In Our Master Project!
Enjoy :)
266. Section Overview

267. Types of Tests
268. Testing Libraries




269. Note: The Next Videos
I know we are waiting a long time to write tests, but we are getting there. The next videos will cover a few more topics that you may have to revisit after you have finished this section. Don’t worry if you don’t fully understand them yet. I want to make sure that we have a basic understanding of testing before we dive into coding to finish off this section.
Again, watch the next few videos but don’t get hung up if you don’t understand everything. Come back to them once you are done this section and you will see that they will be a lot clearer for you.
270. Unit Tests

271. Integration Tests

272. Automation Testing


273. Final Note On Testing
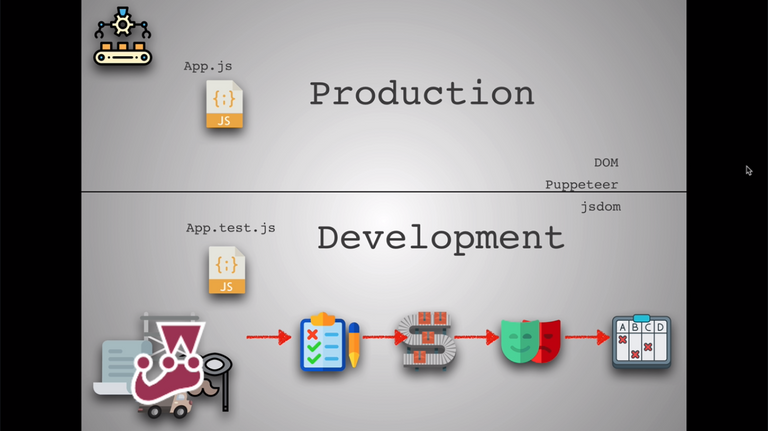
274. Setting Up Jest
npm i -D jest
275. Our First Tests
const googleDatabase = [
"cats.com",
"souprecipes.com",
"flowers.com",
"animals.com",
"catpictures.com",
"myanimalscats.com",
"ilovecats.com"
];
const googleSearch = (searchInput, db) => {
const matches = db.filter(website => {
return website.includes(searchInput);
});
return matches.length > 3 ? matches.slice(0, 3) : matches;
};
// console.log(googleSearch("cat", googleDatabase));
module.exports = googleSearch;276. Writing Tests
const googleSearch = require("./script.js");
const dbMock = [
"dog.com",
"cheese.com",
"ratpoison.com",
"ilovedogs.com",
"dogpictures.com",
"disney.com"
];
describe("googleSearch", () => {
it("silly test", () => {
expect("hello").toBe("hello");
});
it("this is a test", () => {
expect(googleSearch("testtest", dbMock)).toEqual([]);
expect(googleSearch("dog", dbMock)).toEqual([
"dog.com",
"ilovedogs.com",
"dogpictures.com"
]);
});
it("work with undefined and null", () => {
expect(googleSearch(undefined, dbMock)).toEqual([]);
expect(googleSearch(null, dbMock)).toEqual([]);
});
it("does not return more than 3 matches", () => {
expect(googleSearch(".com", dbMock).length).toEqual(3);
});
});277. Asynchronous Tests
const fetch = require("node-fetch");
// const getPeoplePromise = fetch => {
// return fetch("https://swapi.co/api/people")
// .then(res => res.json())
// .then(data => {
// console.log(data);
// return {
// count: data.count,
// results: data.results
// };
// });
// };
const getPeople = async fetch => {
const result = await fetch("https://swapi.co/api/people");
const data = await result.json();
console.log(data);
return {
count: data.count,
results: data.results
};
};
console.log(getPeople(fetch));
module.exports = {
getPeople,
getPeoplePromise
};278. Asynchronous Tests 2
const fetch = require("node-fetch");
const swapi = require("./script2");
it("call swapi to get people", done => {
expect.assertions(1);
swapi.getPeople(fetch).then(data => {
expect(data.count).toEqual(87);
done();
});
});
it("call swapi to get people with promise", () => {
expect.assertions(2);
return swapi.getPeoplePromise(fetch).then(data => {
expect(data.count).toEqual(87);
expect(data.results.length).toBeGreaterThan(6);
});
});279. Resources: Jest Cheat Sheet
Moving forward, you should use the Jest Cheat Sheet to help you along as you write tests if you are coding along in the videos. It will also come in handy at the end of this course where you will have to write tests for our robofriends app.
280. Mocks and Spies
const fetch = require("node-fetch");
const swapi = require("./script2");
it("call swapi to get people", done => {
expect.assertions(1);
swapi.getPeople(fetch).then(data => {
expect(data.count).toEqual(87);
done();
});
});
it("call swapi to get people with promise", () => {
expect.assertions(2);
return swapi.getPeoplePromise(fetch).then(data => {
expect(data.count).toEqual(87);
expect(data.results.length).toBeGreaterThan(6);
});
});
it("get people return count and results", () => { const mockFetch = jest.fn().mockReturnValue( Promise.resolve({ json: () => Promise.resolve({ count: 87, results: [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5] }) }) ); return swapi.getPeoplePromise(mockFetch).then(data => { expect(mockFetch.mock.calls.length).toBe(1); expect(mockFetch).toBeCalledWith("https://swapi.co/api/people"); expect(data.count).toEqual(87); expect(data.results.length).toBeGreaterThan(4); });});281. Note: Testing React Apps
In the next videos we will be using the robofriends-pwa GitHub repo as an example for you. You can use my GitHub repository with all of the code here to get started and follow along as we write tests
282. Introduction To Enzyme
npm i --save-dev enzyme enzyme-adapter-react-16
setupTests.js
import { configure } from "enzyme";
import Adapter from "enzyme-adapter-react-16";
configure({ adapter: new Adapter() });283. Snapshot Testing
npm test - To run the test files
npm test -- --coverage - To see the coverage
import { shallow } from "enzyme";
import React from "react";
import Card from "./Card";
it("expect to render Card component", () => {
const cardComponent = shallow(<Card />);
expect(cardComponent.debug()).toMatchSnapshot();
});284. Snapshot Testing + CodeCoverage
import { shallow } from "enzyme";
import React from "react";
import CardList from "./CardList";
it("expect to render CardList component", () => {
const mockRobots = [
{
id: 1,
name: "John Snow",
username: "JohnJohn",
email: "john@gmail.com"
}
];
const cardComponent = shallow(<CardList robots={mockRobots} />);
expect(cardComponent.debug()).toMatchSnapshot();
});285. Testing Stateful Components
import { shallow } from "enzyme";
import React from "react";
import CounterButton from "./CounterButton";
it("expect to render CounterButton component", () => {
const mockColor = "red";
const counterButtonComponent = shallow(<CounterButton color={mockColor} />);
expect(counterButtonComponent.debug()).toMatchSnapshot();
});
it("expect to render CounterButton component", () => {
const mockColor = "red";
const counterButtonComponent = shallow(<CounterButton color={mockColor} />);
counterButtonComponent.find("[id='counter']").simulate("click");
counterButtonComponent.find("[id='counter']").simulate("click");
counterButtonComponent.find("[id='counter']").simulate("click");
expect(counterButtonComponent.state()).toEqual({ count: 4 });
expect(counterButtonComponent.props().color).toEqual("red");
});286. Quick Recap
🌟 Quick recap on the testing libraries
287. Testing Connected Components
288. Testing Connected Components 2
🌟 Separate the Connected component into a Pure component
import { shallow } from "enzyme";
import React from "react";
import MainPage from "./MainPage";
let MainPageComponent;
beforeEach(() => {
const mockProps = {
onRequestRobots: jest.fn(),
robots: [],
searchField: "",
isPending: false
};
MainPageComponent = shallow(<MainPage {...mockProps} />);
});
it("expect to render MainPage component", () => {
expect(MainPageComponent.debug()).toMatchSnapshot();
});
it("filter robots correctly", () => {
const mockProps2 = {
onRequestRobots: jest.fn(),
robots: [
{
id: "1",
name: "John",
email: "john@email.com"
}
],
searchField: "john",
isPending: false
};
const MainPageComponent2 = shallow(<MainPage {...mockProps2} />);
expect(MainPageComponent2.instance().filteredRobots()).toEqual([
{
id: "1",
name: "John",
email: "john@email.com"
}
]);
});
it("filter robots correctly 2", () => {
const mockProps3 = {
onRequestRobots: jest.fn(),
robots: [
{
id: "1",
name: "John",
email: "john@email.com"
}
],
searchField: "a",
isPending: false
};
const filteredRobots = [];
const MainPageComponent3 = shallow(<MainPage {...mockProps3} />);
expect(MainPageComponent3.instance().filteredRobots()).toEqual(
filteredRobots
);
});289. Testing Reducers
import * as reducers from "./reducers";
describe("searchRobots", () => {
const initialStateSearch = {
searchField: ""
};
it("should return the initial state", () => {
expect(reducers.searchRobots(undefined, {})).toEqual({ searchField: "" });
});
it("should handle CHANGE_SEARCHFIELD", () => {
expect(
reducers.searchRobots(initialStateSearch, {
type: "CHANGE_SEARCHFIELD",
payload: "abc"
})
).toEqual({
searchField: "abc"
});
});
});
describe("requestRobots", () => {
const initialRequestRobots = {
robots: [],
isPending: false
};
it("should return the initial state", () => {
expect(reducers.requestRobots(undefined, {})).toEqual(initialRequestRobots);
});
it("should handle REQUEST_ROBOTS_PENDING", () => {
expect(
reducers.requestRobots(initialRequestRobots, {
type: "REQUEST_ROBOTS_PENDING"
})
).toEqual({
robots: [],
isPending: true
});
});
it("should handle REQUEST_ROBOTS_SUCCESS", () => {
expect(
reducers.requestRobots(initialRequestRobots, {
type: "REQUEST_ROBOTS_SUCCESS",
payload: ["abc"]
})
).toEqual({
robots: ["abc"],
isPending: false
});
});
it("should handle REQUEST_ROBOTS_FAILED", () => {
expect(
reducers.requestRobots(initialRequestRobots, {
type: "REQUEST_ROBOTS_FAILED",
payload: "Oops..! Encountered an Error"
})
).toEqual({
robots: [],
isPending: false,
error: "Oops..! Encountered an Error"
});
});
});290. Testing Actions
npm i -D redux-mock-store
import * as actions from "./actions";
import { CHANGE_SEARCHFIELD, REQUEST_ROBOTS_PENDING } from "./constants";
import configureMockStore from "redux-mock-store";
import thunkMiddleware from "redux-thunk";
const mockStore = configureMockStore([thunkMiddleware]);
it("should create an action to search robots", () => {
const text = "BayWatch";
expect(actions.setSearchField(text)).toEqual({
type: CHANGE_SEARCHFIELD,
payload: "BayWatch"
});
});
it("should create an action to request robots", () => {
const store = mockStore();
store.dispatch(actions.requestRobots());
const action = store.getActions();
console.log(action);
expect(action[0]).toEqual({ type: REQUEST_ROBOTS_PENDING });
});291. Section Review
🌟 Testing Section overall Review
292. Testing In Our Master Project
Now that you learned about testing, it’s time to write your own tests now for our Mastery Project!
You can always refer to the github repo in the resources that has tests written for the app (which we have written for you) to see how you might tackle writing tests for certain components, or testing certain features! We have also linked the enzyme documentation in the resources as well for you to refer to, this way you can see what methods you may want to use to test specific features!
One caveat to note, if you want to use the selector based methods in enzyme to target styled-components in a component, just add the .displayName prop to the styled component where it’s equal to the name of the const. Then you can target that displayName as a string that you pass as the selector value. For example:
// header.styles.jsx
export const OptionLink = styled(Link)`
padding: 10px 15px;
cursor: pointer;
`;
OptionLink.displayName = 'OptionLink';
// Header.test.js
describe('test for OptionLink', () => {
wrapper.find('OptionLink') // <= finds OptionLink styled components in wrapper
});Good luck!
Section 30: Bonus: Web-pack + Babel
293. Introduction to Webpack + Babel
Webpack from scratch || WebPack Doc || Regex Buddy || Babel Doc || Babel Loader
npm i webpack webpack-cli
package.json
🌟 New Build Script
"scripts": {
"build": "webpack --mode production"
},npm i @babel/core @babel/preset-env @babel/preset-react babel-loader
webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|jsx)$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader"
}
}
]
}
};.babelrc
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env", "@babel/preset-react"]
}294. Webpack Config
Style Loader || CSS Loader || HTML Webpack Plugin || Webpack Final Lesson Repo
npm i style-loader css-loader html-loader html-webpack-plugin
const HTMLWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|jsx)$/,
exclude: /node_modules/,
use: {
loader: "babel-loader"
}
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ["style-loader", "css-loader"]
},
{
test: /\.html$/,
use: ["html-loader"]
}
]
},
plugins: [new HTMLWebpackPlugin({ template: "./index.html" })]
};🌟 Import react and react-dom error from Webpack?
- Delete package-lock.json
- Delete node_modules
npm inpm start
🌟 NOTE : For some unknown reason, npm might have failed to pull those dependencies
Section 31: Bonus: Build a GatsbyJSBlog
🌟 Get titles for Section 31
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(title => title.textContent);295. Quick Note About This Section
Here’s the truth: I (Andrei) am not the biggest fan of GatsbyJS. The reason is that it involves a lot of configuration and setup. It’s one of those libraries that feels like you’re learning something completely new instead of just writing Javascript. As you go through these videos, you might find yourself saying “this is so different than anything I have done before as a React developer”. Don’t get discouraged. GatsbyJS is a type of library that requires you to go through the documentation and sometimes learn a completely different way of structuring your code which is unique to Gastby. We decided to add this as a bonus to the course, but by no means should you feel let down if you don’t get everything in these videos. Like I said, Gatsby is all about the “GastbyJS way”, and if you don’t understand it completely, it won’t affect you outside of using GatsbyJS.
So focus more on creating a blog as a fun way to end the course instead of understanding every detail. As a professional React developer, you won’t encounter these problems unless you are working directly with Gatsby.
296. Introduction to Gatsby.js
🌟 Gatsby
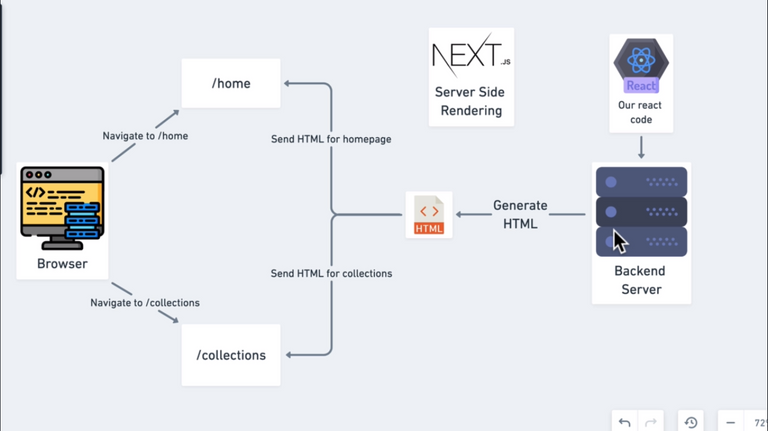
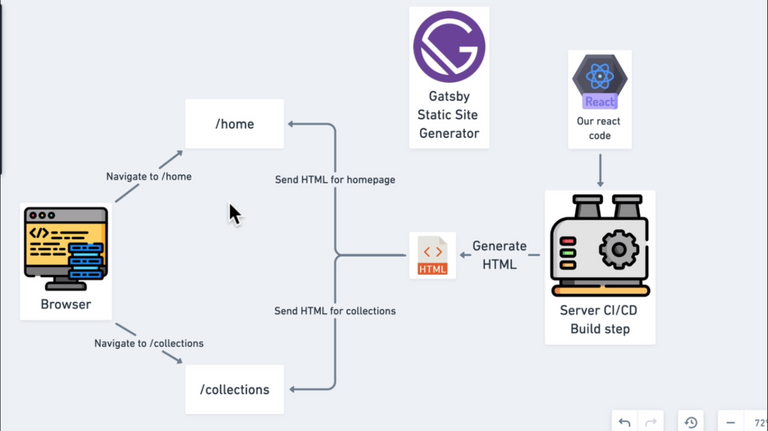
297. Starting a Gatsby Project
Gatsby CLI || Gatsby-starter-blog || Gatsby Plugins
npm i -g gatsby-cli
gatsby new gatsby-blog / npx gatsby new gatsby-blog
npm run develop
298. Gatsby Pages
🌟 Gatsby starter blog walkthrough of components on how things work
299. Gatsby GraphQL + Markdown
gatsby-config.js
module.exports = {
siteMetadata: {
title: `Gatsby Default Starter`,
description: `Kick off your next, great Gatsby project with this default starter. This barebones starter ships with the main Gatsby configuration files you might need.`,
author: `@gatsbyjs`,
},
plugins: [
`gatsby-plugin-react-helmet`,
{
resolve: `gatsby-source-filesystem`,
options: {
name: `images`,
path: `${__dirname}/src/images`,
},
},
{ resolve: `gatsby-source-filesystem`, options: { name: `images`, path: `${__dirname}/src/markdown-pages`, }, }, `gatsby-transformer-sharp`,
`gatsby-plugin-sharp`,
{
resolve: `gatsby-plugin-manifest`,
options: {
name: `gatsby-starter-default`,
short_name: `starter`,
start_url: `/`,
background_color: `#663399`,
theme_color: `#663399`,
display: `minimal-ui`,
icon: `src/images/gatsby-icon.png`, // This path is relative to the root of the site.
},
},
// this (optional) plugin enables Progressive Web App + Offline functionality
// To learn more, visit: https://gatsby.dev/offline
// `gatsby-plugin-offline`,
],
}300. Building Our Blog 1
src/pages/index.js
import React from "react"
import { graphql, Link } from "gatsby"
import Layout from "../components/layout"
import Image from "../components/image"
import SEO from "../components/seo"
const IndexPage = ({
data: {
allMarkdownRemark: { totalCount, edges },
},
}) => (
<Layout>
<SEO title="Home" />
<div>
<h1>Navin's Blog</h1>
</div>
{edges.map(
({
node: {
id,
frontmatter: { date, description, title },
excerpt,
},
}) => (
<div key={id}>
<h2>
{title}-{date}
</h2>
<p>{excerpt}</p>
</div>
)
)}
</Layout>
)
export default IndexPage
export const query = graphql`
query {
allMarkdownRemark {
totalCount
edges {
node {
id
frontmatter {
date
description
title
}
excerpt
}
}
}
}
`301. Building Our Blog 2
🌟 Created a node field for Markdown Files
gatsby-node.js
const { createFilePath } = require("gatsby-source-filesystem")
exports.onCreateNode = ({ node, getNode, actions }) => {
const { createNodeField } = actions
if (node.internal.type === "MarkdownRemark") {
const slug = createFilePath({ node, getNode })
createNodeField({
node,
name: "slug",
value: slug,
})
}
}302. Building Our Blog 3
createPages || createPage || Template Literals
gatsby-node.js
exports.createPages = ({ graphql, actions }) => {
const { createPage } = actions
return graphql(`
{
allMarkdownRemark {
edges {
node {
fields {
slug
}
}
}
}
}
`).then(({ data }) => {
data.allMarkdownRemark.edges.forEach(({ node }) => {
createPage({
path: node.field.slug,
template: "",
})
})
})
}303. Building Our Blog 4
dangerouslysetinnerhtml || path
src/templates/blog-post.js
import React from "react"
import { graphql } from "gatsby"
import Layout from "../components/layout"
export default ({ data }) => {
const post = data.markdownRemark
return (
<Layout>
<div>
<h2>{post.frontmatter.title}</h2>
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: post.html }}>{}</div>
</div>
</Layout>
)
}
export const query = graphql`
query($slug: String!) {
markdownRemark(fields: { slug: { eq: $slug } }) {
html
frontmatter {
title
}
}
}
`304. Building Our Blog 5
styled-components || gatsby-plugin-styled-components || babel-plugin-styled-components || Netlify || Finished Gatsby Blog by Andrei
npm i gatsby-plugin-styled-components styled-components babel-plugin-styled-components
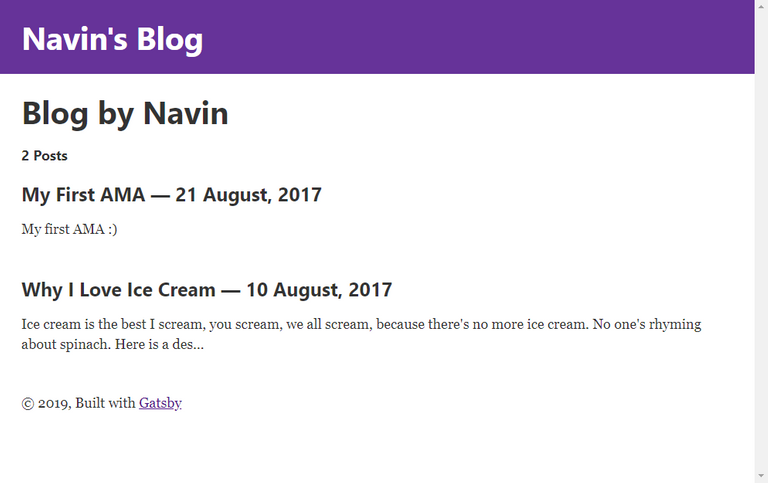
Section 32: Appendix 1: Key Developer Concepts
🌟 Got all Sub Heading by using the below Script
$$(".curriculum-item-link--title--zI5QT").map(text => text.textContent)
304. map()
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4];
myArray.map(el => el + 1);
// [2, 3, 4, 5]
myArray.map(() => "b");
// ["b", "b", "b", "b"]305. Promises
Resolved Promise
const newPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (true) {
setTimeout(() => resolve("I resolved Successfully"), 1000);
} else {
reject("Error - Rejecting");
}
});
newPromise.then(res => console.log(res)).catch(err => console.log(err));
// Promise {<pending>}
// I resolved SuccessfullyRejected Promise
const newPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (false) {
setTimeout(() => resolve("I resolved Successfully"), 1000);
} else {
reject("Error - Rejecting");
}
});
newPromise.then(res => console.log(res)).catch(err => console.log(err));
// Error - Rejecting306. filter()
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4];
myArray.filter(el => true);
// [1, 2, 3, 4]
myArray.filter(el => false);
// []
myArray.filter(el => el > 2);
// [3, 4]307. includes()
includes(<value>, <index>)
Basic
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
myArray.includes(5);
// true
myArray.includes(10);
// false
myArray.includes(5, 6);
// false
myArray.includes(5, 3);
// trueWhy this happens
const myArray = [{ id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, { id: 3 }];
myArray.includes({ id: 1 });
// false
const ob1 = { id: 1 };
const ob2 = { id: 2 };
const ob3 = { id: 3 };
const secArray = [ob1, ob2, ob3];
secArray.includes(ob1);
// trueThis behavior is because of the JavaScript’s difference between Primitive Types and Object Types
- Primitive Types points to the memory of that primitive types.
- Object Types creates a new memory reference.
- Primitive Types are immutable because of the above reason.
- Object Types are mutable.
Primitve Types
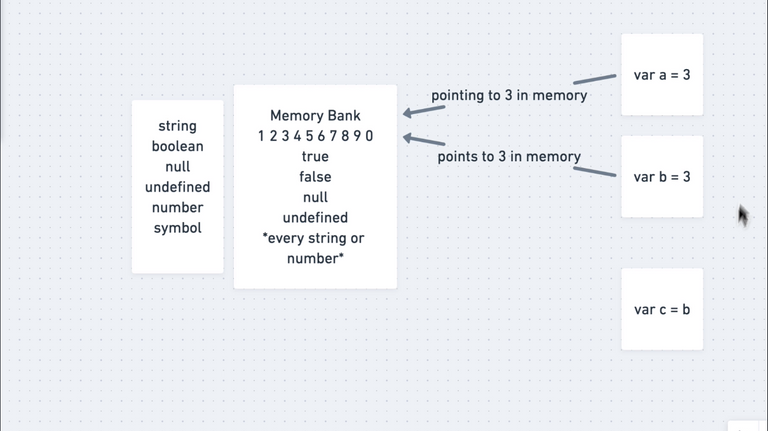
Object Types - Objects & Arrays
308. CWD 2019: Git + GitHub
309. CWD 2019: Git + GitHub 2
310. Async Await
ES6
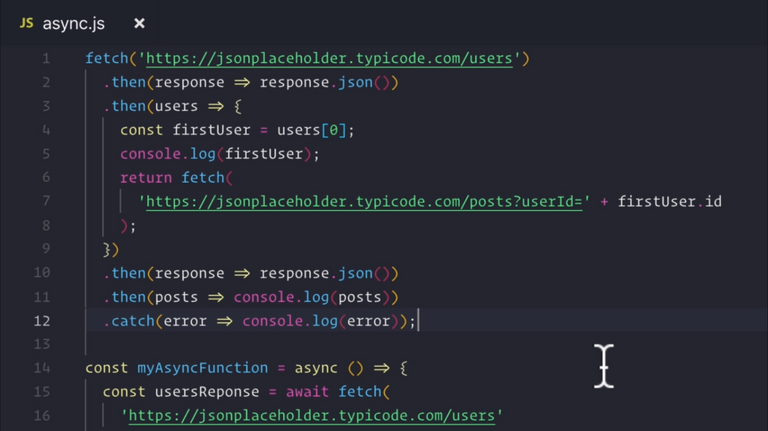
ES7
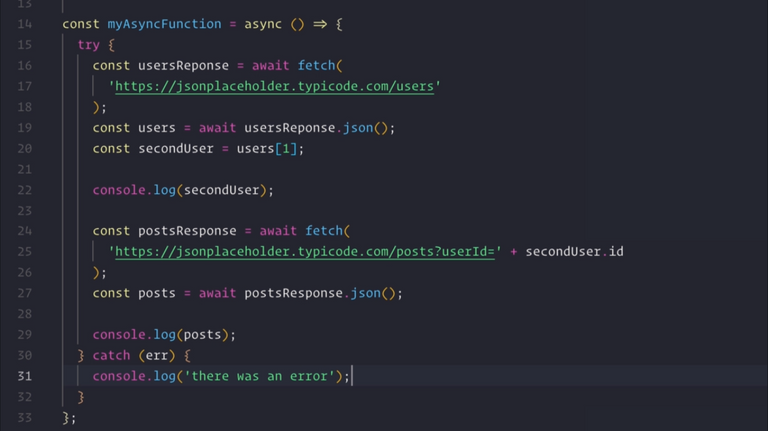
311. find()
🌟 Unlike filter(), find() only gives the first element when the condition matches
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
myArray.find(el => el === 5);
// 5312. reduce()
const myArray = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
myArray.reduce((acc, currEl) => acc + currEl, 0);
// 45313. Memoization
caching repeatedly requested expressions
const cache = {};
const memoizedfunc = n => {
if (n in cache) {
console.log("Cached");
return cache[n];
} else {
console.log("Not Cached");
cache[n] = n + 80;
return cache[n];
}
};
console.log(memoizedfunc(5));
console.log(memoizedfunc(5));
console.log(memoizedfunc(5));314. Currying with Closure
🌟 Function that returns another function utilizing closure to get variables out of the scope and calling them one by one
const currying = a => b => c => a * b * c;
console.log(currying(5)(2)(10));Section 33: Bonus: Coupon Codes +Freebies
- The Complete Web Developer in 2019: Zero to Mastery
- The Complete Junior to Senior Web Developer Roadmap
- Advanced JavaScript Concepts
- Master the Coding Interview: Data Structures + Algorithms