Ultimate Courses - JavaScript Basics
July 31, 2019Course Notes


One of the most recommended courses in Twitter crafted by Todd Motto with Ultimate Courses
The Missing Introduction to Java-Script
The Missing Introduction to JavaScript

Course Intro
Overview of what JavaScript is!! and its features
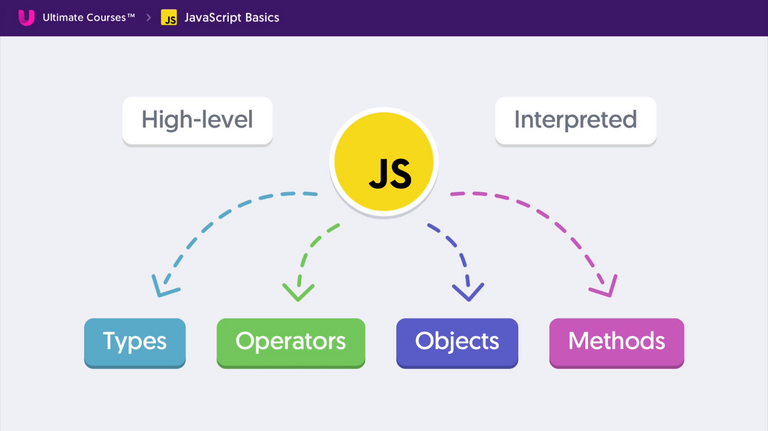
Interpreted vs Compiled Language Differences

- Interpreted Language - No need to be compiled for the execution. Execute directly at Run time.
- Compiled Language - Need a compiler which compiles during the build time.
Multi-Paradigm Language
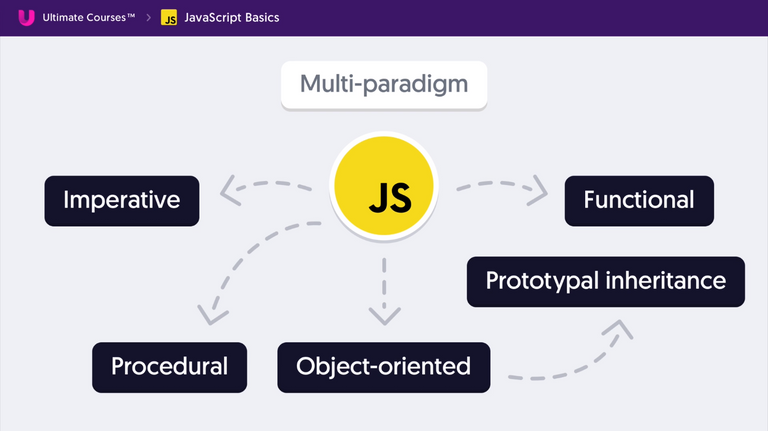
- JavaScript supports multiple styles and designs of writing the code.
History of JavaScript
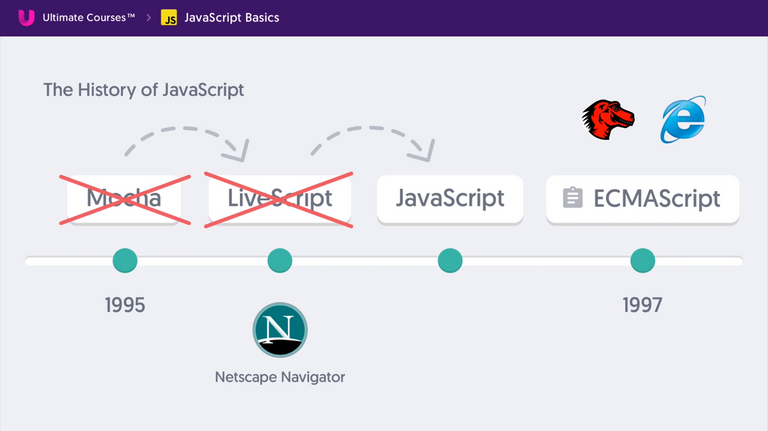
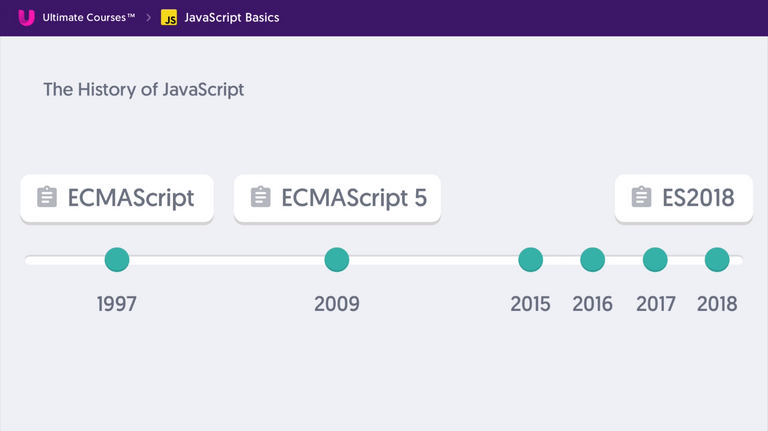
- JavaScript conforms to ECMAScript(ES) Standards.
- Browser vendors should comply to this to reduce the cross-browser bugs.
- Now ECMA Script is being updated yearly.
- Not all browsers supports all the latest ES Features.
Browser Support

- Babel compiles our latest JavaScript code into a code that will be supported by all the browsers including older versions.
- Basically it complies ES2015 and Beyond code into ES5 which is supported by all the browsers.
JavaScript in Front-End vs Back-End
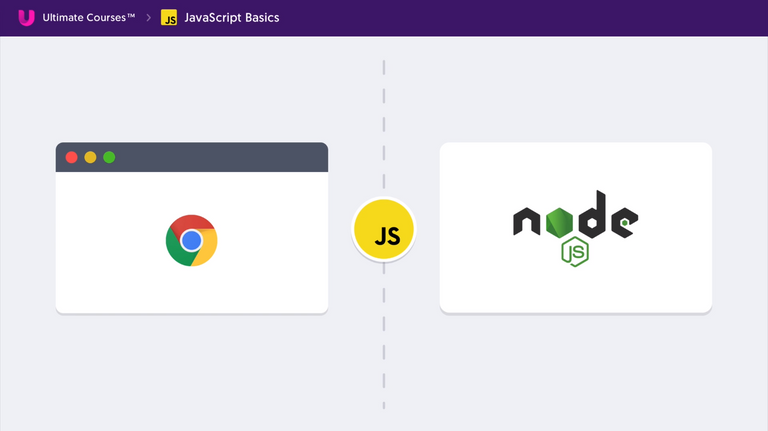
Front End - V8 Engine by Google
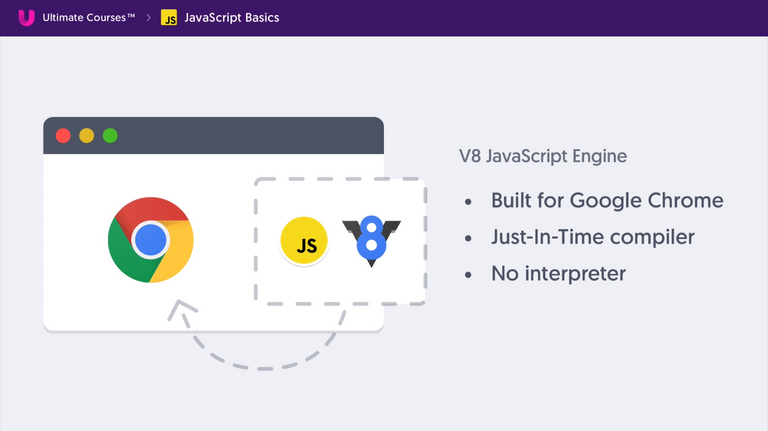
- Browser has something called Document Object Model(DOM).
- JavaScript can interact with DOM Environment to manipulate it.
- One need to learn JavaScript Language along with DOM to fully understand the concept.

Back End - Node JS
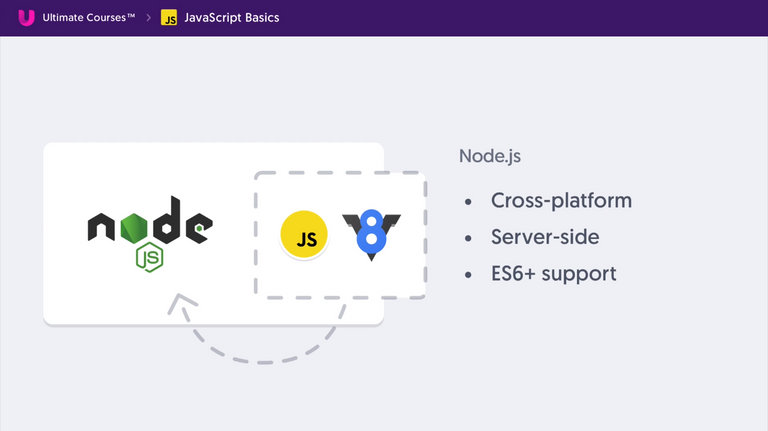
- Node JS has V8 Engine but does not have DOM.
- It has something called Server Side Environment which it can interact with!
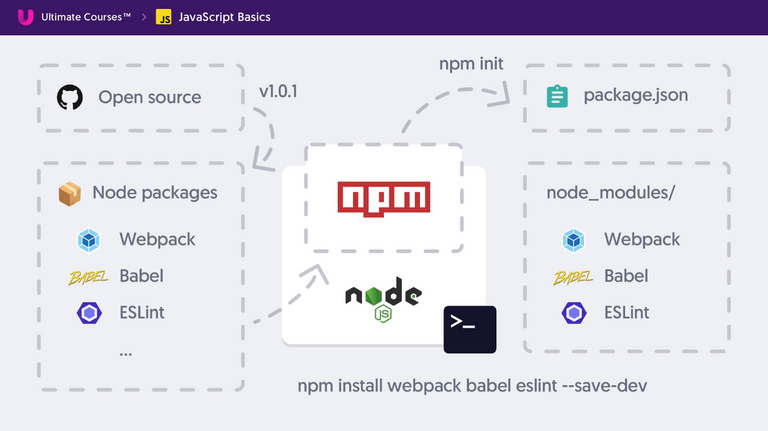
Modern JavaScript

Tooling and Automating JavaScript Development Environtments


External Resources
Node JS | NPM | Babel | Web-Pack | ESLint | MDN Firefox | ECMA International
Variables, Declarations and Assignment

Project Setup
Tools
VS Code | Google Chrome | Node.js
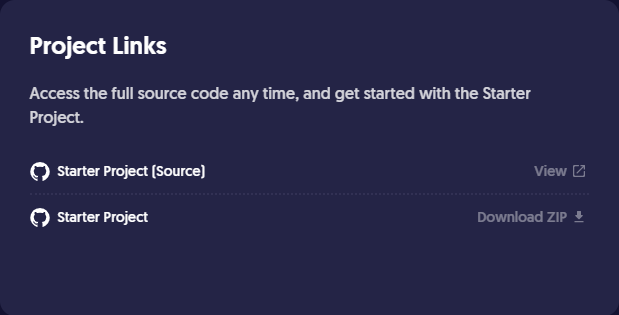
Project Links
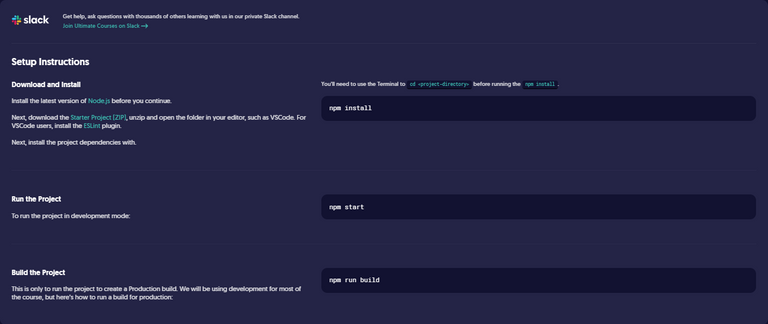
Setup Instructions
Join Ultimate Courses - Slack Channel
Project Walk-through and Install
Project Walk-through
- Clone the starter application from source code - GitHub link.
git clone https://github.com/ultimatecourses/javascript-basics
- Change the current directory to “javascript-basics”.
cd javascript-basics- Now lets start with the
index.html- base of our project.
Path: ./index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Ultimate Courses</title>
</head>
<body>
<header class="header">
<div class="logo">
<div class="logo-ultimate"></div>
<p class="logo-name">Ultimate Courses<span>™</span></p>
</div>
</header>
<div id="app"></div>
</body>
</html>- We will be seeing the source code here and console window from Chrome’s Dev-Tools to debug our application.
Path: ./src/index.js
import "../assets/css/style.css";
const app = document.getElementById("app");
app.innerHTML = "<h1>JavaScript Basics</h1>";- Imported the css file into this java script file
- We are now accessing the HTML’s DOM Element
<div id="app"></div>usingdocument.getElementById('app'). - Setting it’s
innerHTMLas<h1>JavaScript Basics</h1>. assestsfolder has all the required files for styling(CSS), font and images
.babelrchas the recommended basic configuration required by the Babel.
Path: ./.babelrc
{
"presets": ["@babel/preset-env"]
}.eslint.jsonis a powerful tool to help us with the Code Quality.- Display’s errors in case of a bad quality of code written as red squiggly.
Path: ./.eslint.json
{
"env": {
"browser": true,
"es6": true
},
"extends": "eslint:recommended",
"globals": {
"Atomics": "readonly",
"SharedArrayBuffer": "readonly"
},
"parserOptions": {
"ecmaVersion": 2018,
"sourceType": "module"
},
"rules": {
"no-console": "off"
}
}Path: ./webpack.config.babel.js
import path from "path";
import HtmlWebpackPlugin from "html-webpack-plugin";
export default {
entry: path.join(__dirname, "src/index.js"),
output: {
path: path.join(__dirname, "dist"),
filename: "[name].bundle.js"
},
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.js/,
exclude: /(node_modules)/,
use: ["babel-loader", "eslint-loader"]
},
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: ["style-loader", "css-loader"]
},
{
test: /\.(png|svg|jpg|gif)$/,
use: ["file-loader"]
},
{
test: /\.(woff|woff2|eot|ttf|otf)$/,
use: ["file-loader"]
}
]
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: path.join(__dirname, "index.html"),
favicon: "assets/img/favicon.png"
})
],
stats: "minimal",
devtool: "source-map",
mode: "development",
devServer: {
open: false,
contentBase: "./dist",
inline: true,
port: 8080,
host: "0.0.0.0"
}
};- Let’s breakdown the web-pack file.
- Basic setup
entrypath for giving our entry js file andoutputpath to give out the compiled code. - Then rule with couple of loaders in bottom to top order telling how web-pack should compile our application.
HtmlWebpackPluginto include ourindex.htmlfile as the template andfaviconpath to be generated and added to the final compiledindex.htmldevServerto configure our development server.modecan be set to development/production.
Path: ./package.json
{
"name": "javascript-basics",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "Starter Repo for JavaScript Basics",
"main": "index.js",
"repository": {
"type": "git",
"url": "git://github.com/ultimatecourses/javascript-basics.git"
},
// Scripts that can be run using `npm`
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"watch": "webpack --watch", // `npm run watch`
"start": "webpack-dev-server", // `npm start`
"build": "webpack" // `npm run build`
},
"author": "Ultimate Courses",
"license": "MIT",
// Dev Dependencies that your project relies on!!!
"devDependencies": {
"@babel/core": "^7.4.3", // '^'-> Satisfies Latest Version
"@babel/preset-env": "7.4.3", // Fixed Version
"@babel/register": "^7.4.0",
"babel-loader": "^8.0.5",
"css-loader": "^2.1.1",
"eslint": "^5.16.0",
"eslint-loader": "^2.1.2",
"eslint-plugin-import": "^2.17.1",
"file-loader": "^3.0.1",
"html-webpack-plugin": "^3.2.0",
"style-loader": "^0.23.1",
"webpack": "^4.30.0",
"webpack-cli": "^3.3.0",
"webpack-dev-server": "^3.3.1"
}
}Install
- Dependencies are the packages that are available in NPM registry.
- Install them using
npm install. - Creates a
package-lock.jsonwhich should be committed to the version control andnode_moduleswhich has all the files requires by our dependencies. - This is useful to check the integrity of these packages.
- Run
npm startto start the application by the commandwebpack-dev-server. - This command runs the code belongs to its dependency.
- Spins up the application in
http://0.0.0.0:8080/. - Build the project with
npm build.distfolder contains all compiled code is generated.
Extras
Path: ./gitignore
node_modules
dist/*- Remove the
.gitfolder andgit initto make your own git container and commit the files. - Our
node_modulesanddistdirectory will be excluded from git watch.
Next we will see more about the project.
Hello <script> World
- Lets learn about the
<script>tag. - It is an HTML element which holds our javascript code.
- It has two attributes
srcandtypeand<noscript>tag. src- path to your JavaScript file.type-text/javascriptwhich means that this script is a JavaScript
<script>
console.log("Hello World!!");
</script>- Output can viewed in Chrome’s Dev-Tools at Console Window.
scripttags can be placed inheadtag or in the end ofbodytag.noscript- to inform the user about the disabled JavaScript.
<noscript>Your Javascript is disabled!!</noscript>- Above code will be executed only when the browsers does not have the JavaScript Enabled.
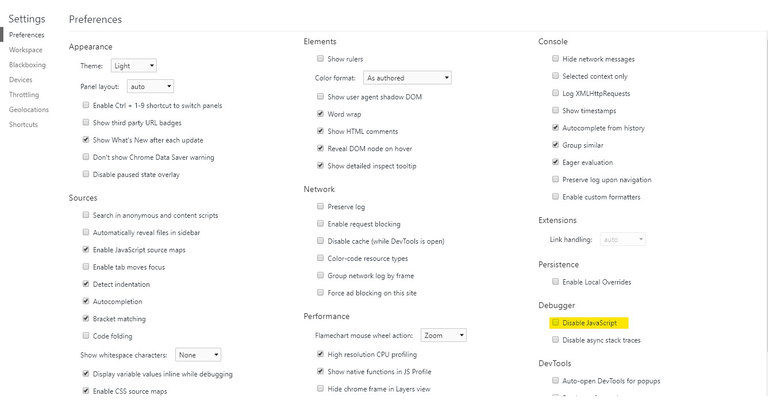
Note: JavaScript can be disabled manually in the browser by going to the devTools->Preference->Debugger-> Click the checkbox
Disable JavaScript
Understanding var and Hoisting
- Learned about the
varreserved keywords. - Declarations
- Initialization
undefined- More clearance on this- Hoisting - whatever or wherever a variable is declared, JavaScript will take and declare them at the top of the file.
// Declaration
var a;
console.log(a); // `undefined`
// Initialization
a = 2;
console.log(a); // 2Block scoping and let
- Scoped - Within the nearest block.
- Will not be hoisted.
- Only available within the respective block.
- Can declare variables of same name in the same file within different block.
// `let` declared and initialized
console.log(a); // ReferenceError: Cannot access 'a' before initialization
let a = 5;
console.log(a); // 5Variables with const
- Scoped
- Not bind-able to another value again
- Immutable - the variable itself
- Mutable - Objects of that variable
const a = 10;
console.log(a); // 10
a = 11; // Assignment to constant variable.Conditional Logic
Truthy and Falsy Values
Intro
console.log(1 == 1); // true
console.log(1 === 1); // true
console.log(1 == "1"); // true
console.log(1 === "1"); // falseTruthy
console.log(!!true)
console.log(Boolean(true)
console.log(!!{})
console.log(!![])
console.log(!!new Date())
console.log(!!"0")
console.log(!!42)
console.log(!!-42)
console.log(!!43.3)
console.log(!!-43.3)Falsy
console.log(!!false)
console.log(Boolean(false)
console.log(!!0)
console.log(!!"")
console.log(!!null)
console.log(!!undefined)
console.log(!!NaN)If, Else If and Else Statements
const condition = true;
if (condition) {
console.log("Yes"); // Yes
} else {
console.log("No");
}
// OR
if (condition) console.log("Yes");
// Yes
else console.log("No");
// More realistic example
const number = 99;
let result; // undefined
if (number === 1) {
result = "One";
} else if (number === 99) {
result = "Ninety-Nine";
} else if (number === 1000) {
result = "One Thousand";
} else {
result = "No Match";
}
console.log(result); // Ninety-NineTernary Operator
const number = 1;
const result = "The Number is: " + (number === 1 ? "One" : "No Match");
console.log(result); // The Number is: One
// Nested Ternary Expressions
const anotherNumber = 99;
const anotherResult =
anotherNumber === 1
? "One"
: anotherNumber === 99
? "Ninety-Nine"
: anotherNumber === 1000
? "One Thousand"
: "No Match";
console.log(anotherResult);
Ninety - Nine;Switch Statements
const number = 1;
let result;
switch (number) {
case 1: {
const text = "One";
result = text;
break;
}
case 99: {
const text = "Ninety-Nine";
result = text;
break;
}
case 1000:
result = "One Thousand";
break;
default:
result = "No Match";
}
console.log(result); // OneNumbers In-Depth

Number Literal, Function and Constructor Syntax
// literal
const literalNumber = 99;
console.log(literalNumber); // 99
// function syntax
// perform a type-conversion in a non-constructor context
console.log(Number(55)); // 55
console.log(Number("33")); // 33
console.log(Number("44px")); // NaN
// constructor syntax, creates a wrapper Object
// avoid using it
console.log(new Number("44px")); // Number {NaN}Integers and Floating Points
console.log(0.1 + 0.2); // 0.30000000000000004
const price = 9.33;
const quantity = 3;
console.log(price * quantity); // 27.990000000000002
const anotherPrice = 9.33 * 100;
const anotherQuantity = 3;
console.log((anotherPrice * anotherQuantity) / 100); // 27.99Parsing Strings to Numbers
console.log(parseInt("55px", 10)); // 55
console.log(parseFloat("55.9999px") * 10); // 559.999
console.log(Number("55e10")); // 550000000000
console.log(Number("55.9999")); // 55.9999
console.log(9 + +"99.5555"); // 108.5555Understanding Not-a-Number
const result = Number("55px");
// isNaN "NaN"
console.log(isNaN(result)); // true
console.log(isNaN("I am a String!")); // true
console.log(Number.NaN); // NaN
console.log(Number.isNaN(Number.NaN)); // true
console.log(Number.isNaN(result)); // true
console.log(Number.isNaN("I am another String!")); // false
console.log(Number.isInteger(66)); // trueNumbers and Immutability
const immutableNumber = 99;
// Just the immutablenumber is copied - Not referenced
let referencedNumber = immutableNumber;
referencedNumber = 44;
console.log(immutableNumber); // 99
console.log(referencedNumber); // 44Correctly Type-Checking Numbers
console.log(typeof 99.66); // Number
console.log(99 instanceof Number); // false
console.log(Number("99") instanceof Number); // false
console.log(new Number("99") instanceof Number); // true
// Most useful way of TypeChecking
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(99).slice(8, -1) === "Number"); // trueExploring Number Methods
console.log(Number.prototype); // Number Object
console.log(parseFloat((99.12345678).toFixed(4))); // 99.1234
console.log((99.12345678).toPrecision(5)); // "99.123"
console.log(new Number(99).valueOf()); // 99Strings In-Depth
String Literal, Function and Constructor Syntax
console.log('Pizza "Hello!"'); // Pizza "Hello!"
const pizza = "Pepperoni";
console.log("Pizza is: " + pizza + "!"); // Pizza is: Pepperoni!
/* Pizza is:
* Pepperoni!
*/
console.log(`
Pizza is:
${pizza}!
`);
console.log(String(55 + 11), 55 + "11"); // 66 5511
console.log(String({ name: "Pepperoni" })); // [object Object]
console.log(String([1, 2, 3, 4])); // 1,2,3,4
console.log(new String(55)); // String {"55"}String Properties and Indexes
console.log(new String(5599)); // String {"5599"}
console.log("Pepperoni".length); // 9
const pizza = "P e p p e r o n i";
console.log(pizza[0], pizza[pizza.length - 1], pizza.length); // P i 17Strings and Immutability
const immutableString = "I shall not change!";
const uppercaseString = immutableString.toUpperCase();
console.log(immutableString, uppercaseString); // I shall not change! I SHALL NOT CHANGE!Correctly Type-Checking Strings
console.log(typeof "Pepperoni"); // string
console.log("Pepperoni" instanceof String); // false
console.log(new String("Pepperoni") instanceof String); // true
console.log(String("Pepperoni") instanceof String); // false
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call("Pepperoni")); // [object string]Exploring String Methods
console.log(String.prototype); // String Object
console.log("Pepperoni".indexOf("P")); // 0
console.log("Pepperoni".includes("P")); // true
console.log("Pepperoni".replace("oni", "fire")); // Pepperfire
console.log("Pepperoni".replace(/oni$/, "fire")); // Pepperfire
console.log("Pepperoni".slice(2, -3)); // pper
console.log("Pepperoni~Plain".split("~")[1]); // Plain
console.log("Pepperoni~Plain".split(/~/)[1]); // Plain
console.log("Pepperoni~Plain".split());
// (15) ["P", "e", "p", "p", "e", "r", "o", "n", "i", "~", "P", "l", "a", "i", "n"]
console.log(" 4444 5555 6666 7777 ".trim()); // 4444 5555 6666 7777
console.log(" 4444 5555 6666 7777 ".replace(/\s/g, "")); // 4444555566667777Boolean In-Depth

Boolean Literal, Function and Constructor Syntax
console.log(true, false); // true false
const arg = "X";
console.log(Boolean(arg)); // true
console.log(!!arg); // true
console.log(Boolean([])); // true
console.log(Boolean({})); // true
console.log(new Boolean(arg)); // trueCorrectly Type-Checking Boolean
console.log(typeof false); // boolean
console.log(true instanceof Boolean); // false
console.log(new Boolean("X") instanceof Boolean); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(true)); // [object Boolean]Functions In-Depth

Function Declarations and Expressions
// hoisting
console.log(makeCar); // makeCar()
console.log(makeCarExpression); // undefined
console.log(makeCarArrow); // undefined
console.log(makeCarArrowShorthand); // undefined
// 1: Function Declaration
function makeCar() {
console.log("Making car...");
}
makeCar(); // Making car...
// 2: Function Expression (anonymous or named)
const makeCarExpression = function myFunction() {};
console.log(makeCarExpression.name); // makeCarExpression
// 3: Arrow Function
const makeCarArrow = () => {
console.log("Making car inside Arrow...");
};
makeCarArrow(); // Making car inside Arrow...
const makeCarArrowShorthand = () => console.log("Short");
makeCarArrowShorthand(); // ShortFunction Parameters and Defaults
// name = parameter
function makeCar(name = "Porsche") {
// name = name || 'Porsche';
// if (!name) {
// name = 'Porsche';
// }
console.log(`Making car: ${name.toUpperCase()}`);
}
// strings = arguments
makeCar("Porsche"); // Making car: PORSCHE
makeCar("Ferrari"); // Making car: FERRARI
makeCar(); // Making car: PORSCHERest Parameters and Arguments
function makeCarPrice() {
console.log(arguments, Array.isArray(arguments)); // Arguments(5) || false
const total = Array.from(arguments).reduce((prev, next) => {
return prev + next;
});
console.log(`Total: ${total}USD`); // Total: 275USD
}
makeCarPrice(11, 44, 55, 99, 66);
function makeCarPriceRest(...params) {
console.log(Array.isArray(params)); // true
const total = params.reduce((prev, next) => prev + next);
console.log(`Total: ${total}USD`); // Total: 319USD
}
makeCarPriceRest(99, 88, 77, 11, 44);Function Return Values
function makeCarPrice(...params) {
const total = params.reduce((prev, next) => prev + next);
return total;
}
const makeCarPriceArrow = (...params) =>
params.reduce((prev, next) => prev + next);
console.log(`Total: ${makeCarPrice(11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66)}`); // Total: 231
console.log(`Total: ${makeCarPriceArrow(99, 77, 44)}`); // Total: 220Function Closures and Scope
function makeCarPartID(id) {
const theId = `CAR_PART_${id}`;
return function(name) {
return `${theId}_${name.toUpperCase()}`;
};
}
const carPartId = makeCarPartID("x8YdsZ12");
console.log(carPartId("Left Door")); // CAR_PART_x8YdsZ12_LEFT DOOR
console.log(carPartId("Right Door")); // CAR_PART_x8YdsZ12_RIGHT DOOR
console.log(carPartId("Windscreen")); // CAR_PART_x8YdsZ12_WINDSCREEN
const anotherCarPartId = makeCarPartID("7hs9zSaq0");
console.log(anotherCarPartId("Left Door")); // CAR_PART_7hs9zSaq0_LEFT DOOR
console.log(anotherCarPartId("Right Door")); // CAR_PART_7hs9zSaq0_RIGHT DOOR
console.log(anotherCarPartId("Windscreen")); // CAR_PART_7hs9zSaq0_WINDSCREENImmediately-Invoked Function Expressions (IIFE)
const carPartId = (function(id) {
const theId = `CAR_PART_${id}`;
return function(name) {
return `${theId}_${name}`;
};
})("x8YdsZ12");
console.log(carPartId("Left Door")); // CAR_PART_x8YdsZ12_LEFT DOOR
console.log(carPartId("Right Door")); // CAR_PART_x8YdsZ12_RIGHT DOOR
console.log(carPartId("Windscreen")); // CAR_PART_x8YdsZ12_WINDSCREENFunctions and Callbacks
function carPartId(name, fn) {
const theId = `CAR_PART_x8zOsl`;
return fn(`${theId}_${name}`);
}
const carPart = carPartId("Left Door", function(id) {
return `Car Part ID: ${id}`;
});
console.log(carPart);Functions and “this”
const firstCar = { id: "x8KszK0" };
const secondCar = { id: "bc90slqa" };
const thirdCar = { id: "h9sNsa" };
function carPartId(name, quantity) {
console.log(`${this.id}_${name}_${quantity}`);
}
const boundThirdCar = carPartId.bind(thirdCar);
boundThirdCar("Windscreen", 99); // h9sNsa_Windscreen_99
boundThirdCar("Exhaust", 9); // h9sNsa_Exhaust_9
// call = c = commas
carPartId.call(firstCar, "Left Door", 12); // x8KszK0_Left Door_12
// apply = a = array
carPartId.apply(secondCar, ["Right Door", 21]); // bc90slqa_Right Door_21Objects In-Depth

Object Literal, Function and Constructor Syntax
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
// Mutable - Referenced to the original
const drinkReference = drink;
drinkReference.name = "Peach";
// Referencing the same object
console.log(drink === drinkReference); // true
// Two different object
console.log({} === {}); // false
console.log(new Object() instanceof Object); // true
// Object() calls new Object() internally
console.log(Object() instanceof Object); // true
console.log({} instanceof Object); // trueProperties, Methods and Values
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: 99,
getDrinkDetails() {
return `Drink ${this.name} (${this.price})`;
},
"abc 123": "I am the value!",
100: "I am a number!"
};
const myId = "id";
console.log(drink[myId]); // xhs8Pla
console.log(drink.name); // Lemonade
console.log(drink.price); // 99
console.log(drink["abc 123"]); // I am the value!
console.log(drink[100]); // I am a number!Shorthand Properties and Methods
const id = "xhs8Pla";
const name = "Lemonade";
const price = 99;
const someKey = "name";
const drink = {
id,
[someKey]: name,
price,
getDrinkDetails() {
return `Drink ${this.name} (${this.price})`;
}
};
console.log(drink); // {id: "xhs8Pla", name: "Lemonade", price: 99, getDrinkDetails: ƒ}Destructuring Object Properties
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
const myDrinkId = drink.id;
const myDrinkName = drink.name;
const myDrinkSalePrice = drink.price.sale;
console.log(myDrinkId, myDrinkName, myDrinkSalePrice);
// xhs8Pla Lemonade 99
// const id = 1234;
const {
id: myId,
price: { full },
...rest
} = drink;
const { sale, full: fullPrice } = drink.price;
console.log(sale, fullPrice); // 99 129
console.log(myId, name, full, rest);
// xhs8Pla previewFrame 129 {name: "Lemonade"}Property and Value Existence Checking
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
// hasOwnProperty() {
// return false;
// },
};
// value exists
if (drink.id) {
console.log(drink.id); // xhs8Pla
}
for (const prop in drink) {
if (drink[prop] === "Lemonade") {
console.log(drink[prop]); // Lemonade
}
}
const hasLemonade = Object.values(drink).includes("Lemonade");
console.log(hasLemonade); // true
// property exists
console.log(drink.hasOwnProperty("name")); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(drink, "name")); // true
console.log(Object.keys(drink).includes("name")); // trueAdding and Updating Object Properties
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
// drink.brand = 'My Drinks Co.';
// drink.name = 'Peach';
function propUpdate(prop, value) {
drink[prop] = value;
}
propUpdate("brand", "My Drinks Co.");
propUpdate("name", "Lime");
console.log(drink);
// {id: "xhs8Pla", name: "Lime", price: {…}, brand: "My Drinks Co."}Removing Object Properties
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
// slow
// delete drink.id;
drink.id = undefined;
if (drink.id) {
console.log("Has ID...");
}
console.log(drink.hasOwnProperty("id")); // true
const { price, ...rest } = drink;
console.log(price, rest, drink);
// {sale: 99, full: 129} {id: undefined, name: "Lemonade"} {id: undefined, name: "Lemonade", price: {…}}Shallow and Deep Object Cloning
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
// shallow copies
// const drinkClone = Object.assign({}, drink);
// const drinkClone = { ...drink };
// deep copy
const drinkStringified = JSON.stringify(drink);
const drinkClone = JSON.parse(drinkStringified);
drinkClone.id = "abcd";
drinkClone.price.sale = 79;
console.log(drink);
// {id: "xhs8Pla", name: "Lemonade", price: {…}}Merging Objects
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade"
};
const price = {
sale: 99,
full: 129
};
// const mergedDrink = Object.assign({}, drink, { price });
const mergedDrink = { ...drink, ...{ price } };
console.log(drink, price);
// {id: "xhs8Pla", name: "Lemonade"} {sale: 99, full: 129}
console.log(mergedDrink);
// {id: "xhs8Pla", name: "Lemonade", price: {…}}Correctly Type-Checking Objects
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
function getType(obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString
.call(obj)
.slice(8, -1)
.toLowerCase();
}
console.log(typeof drink); // object
console.log(typeof [1, 2, 3]); // object
console.log(typeof null); // object
console.log({} instanceof Object); // true
console.log([] instanceof Object); // true
console.log(null instanceof Object); // false
console.log(getType(drink)); // object
console.log(getType(null)); // null
console.log(getType([])); // arrayImperative Object Iteration
const drink = {
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
const drinkWithId = Object.create(drink);
drinkWithId.id = "xhs8Pla";
console.log("name" in drinkWithId);
for (const prop in drinkWithId) {
if (drinkWithId.hasOwnProperty(prop)) {
console.log(prop, drinkWithId[prop]);
}
}
console.log("-----");
// for..in
for (const prop in drink) {
const value = drink[prop];
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(value) === "[object Object]") {
for (const key in value) {
console.log(key);
}
}
}
/* true
* id xhs8Pla
* ---
* sale
* full
*/Declarative Object Iteration
const drink = {
id: "xhs8Pla",
name: "Lemonade",
price: {
sale: 99,
full: 129
}
};
Object.keys(drink).forEach(prop => console.log(drink[prop]));
/* xhs8Pla
* Lemonade
* {sale: 99, full: 129}
*/
console.log(Object.entries(drink));
// (3) [Array(2), Array(2), Array(2)]
console.log(drink);
// {id: "xhs8Pla", name: "Lemonade", price: {…}}Arrays In-Depth
Array Literal, Function and Constructor Syntax
const drinks = ["Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach"];
const drinksReference = drinks;
console.log(drinks); // Array(3)
// Mutated
console.log(drinks === drinksReference); // true
console.log(new Array("Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach")); // Array(3)
console.log(Array("Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach")); // Array(3)Properties, Indexes and Elements
const drinks = ["Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach"];
drinks[0] = "Diet Lemonade";
// drinks['favourite'] = 'Cola';
console.log(drinks); // (3) ["Diet Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach"]
console.log(drinks[0]); // Diet Lemonade
console.log(drinks[drinks.length - 1]); // Peach
drinks.length = 0;
// drinks.splice(0, drinks.length);
console.log(drinks); // []Multi-dimensional Arrays
const drinks = [["Lemonade", 99], ["Lime", 99], ["Peach", 89]];
console.log(`Drink: ${drinks[0][0]}, Price: ${drinks[0][1]}`);
// Drink: Lemonade, Price: 99Destructuring Arrays
const drinks = [["Lemonade", 99], ["Lime", 99], ["Peach", 89]];
const [one, [, b], ...rest] = drinks;
console.log(one, b, rest); // ["Lemonade", 99] 99 [Array(2)]Adding Array Elements
const drinks = ["Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach"];
// beginning
// drinks.unshift('Water'); // mutable
// newDrinksArray.length = 0;
console.log(["Water", ...drinks]); // immutable
// ["Water", "Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach"]
// middle
const index = 1;
// drinks.splice(index, 0, 'Cola'); // mutable
console.log([
...drinks.splice(0, index),
"Mojito",
...drinks.splice(index - 1)
]);
// ["Lemonade", "Mojito", "Lime", "Peach"]
// end
// drinks.push('Cola'); // mutable
console.log([...drinks, "Beer"]); // immutable // ["Beer"]
console.log(drinks); // []Removing Array Elements
const drinks = ["Lemonade", "Lime", "Peach"];
// beginning
// const removed = drinks.shift();
// end
const removed = drinks.pop();
console.log(removed); // Peach
// slice = anywhere
const index = drinks.length - 1;
const newDrinks = [...drinks.slice(0, index), ...drinks.slice(index + 1)];
console.log(newDrinks);
console.log(drinks);Shallow and Deep Array Cloning
const drinks = [["Lemonade", 99], ["Lime", 99], ["Peach", 89]];
// const drinksClone = [...drinks];
// const drinksClone = drinks.slice();
// const drinksClone = Array.from(drinks);
const drinksClone = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(drinks));
drinksClone[0][1] = 1000;
console.log(drinks);
/* 0: (2) ["Lemonade", 99]
* 1: (2) ["Lime", 99]
* 2: (2) ["Peach", 89]
*/Merging Arrays
const drinks = [["Lemonade", 99], ["Lime", 99]];
const newDrinks = ["Peach", 89];
// const merged = drinks.concat(newDrinks); // Immutable
const merged = [newDrinks, ...drinks];
console.log(merged);
console.log(drinks);
console.log(newDrinks);Reversing and Sorting Arrays
const drinks = [
{ name: "Lemonade", price: 79 },
{ name: "Peach", price: 99 },
{ name: "Lime", price: 89 }
];
console.log(drinks.reverse());
// 0: {name: "Lime", price: 89}
// 1: {name: "Peach", price: 99}
// 2: {name: "Lemonade", price: 79}
console.log(drinks.sort((a, b) => b.price - a.price));
// 0: {name: "Peach", price: 99}
// 1: {name: "Lime", price: 89}
// 2: {name: "Lemonade", price: 79}Correctly Type-Checking Arrays
console.log(typeof []); // object
console.log([] instanceof Array); // true
console.log(new Array() instanceof Array); // true
console.log(Array.isArray([1, 2, 3, 4])); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([])); // [object Array]Modules and JavaScript (Coming Soon)
